- Home
- >
News
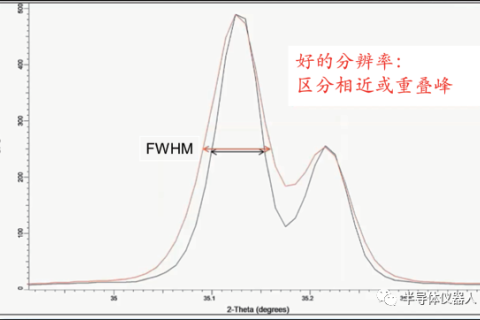
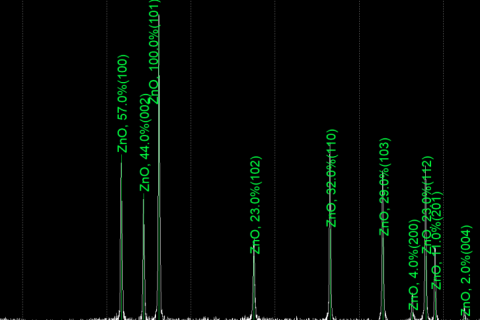
As one of the important means of material structure characterization, XRD is widely used in materials, physics, chemistry, medicine and other fields.
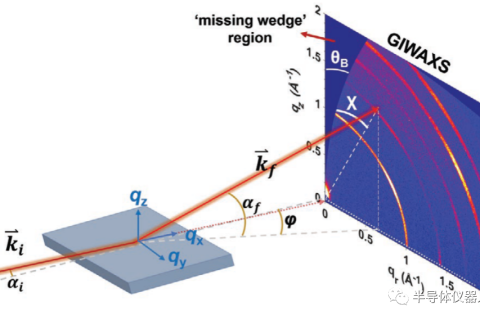
GIWAXS is a technique to characterize the internal microstructure of thin film samples. The corresponding structure size is between 10nm and 1um, so it is widely used to characterize the crystallization inside solar thin film cells.
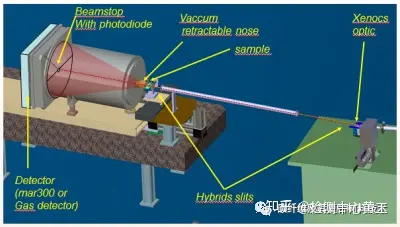
X-ray diffractometer is a device that uses the principle of interaction between X-rays and substances to obtain information such as crystal structure and lattice constant of substances by measuring the diffraction Angle and intensity of X-rays in substances.
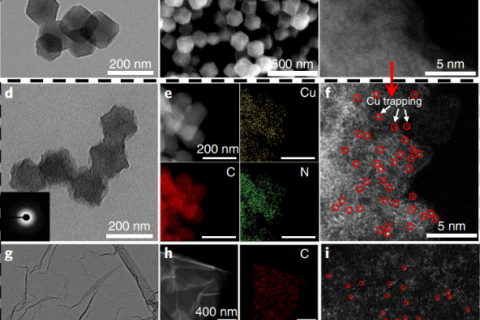
Characterization methods of copper monatomic catalysts are often used to determine their structure and properties, and the following are several common characterization methods.
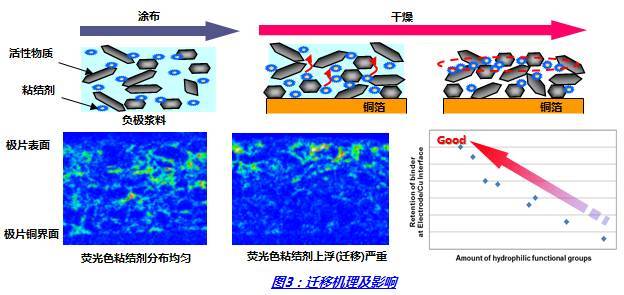
Binder is a polymer compound used in electrode making to adhere the active substance to the collector fluid. The main function is to bond and maintain active substances.
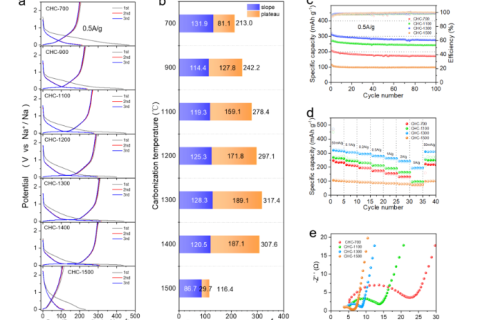
In this paper, a series of hard carbon materials with adjustable structure were prepared using chitosan as carbon source, and the relationship between the evolution of hard carbon structure and the properties of sodium storage was analyzed.
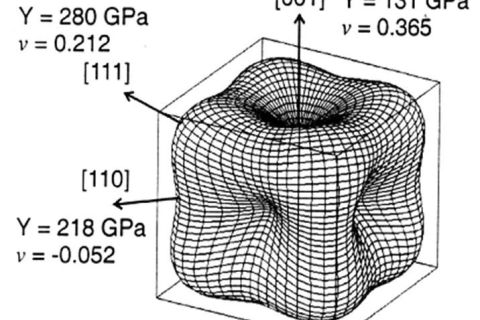
Many materials through rolling, extrusion and other deformation processes, or even if not deformed, the grains in the polycrystal show more or less statistical uneven distribution, this organizational structure is called texture.
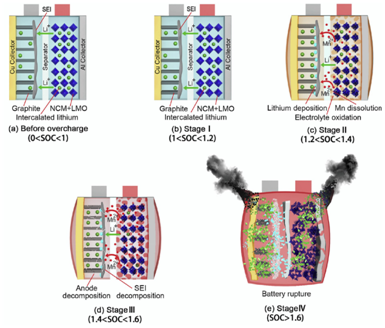
The method of assisting internal stress without additional energy proposed in this paper provides an economical and convenient new strategy for improving battery reaction dynamics.
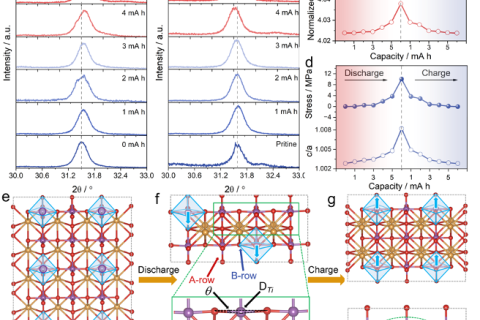
X-ray diffraction technology is widely used in the research of lithium-ion batteries. XRD is a conventional method for qualitative and quantitative analysis of phases in materials.
The application of new technologies and new products such as 5G, big data, and artificial intelligence will bring a huge semiconductor market demand, and global semiconductor equipment spending has entered an upward cycle.