
Principle and application of small Angle X-ray scattering
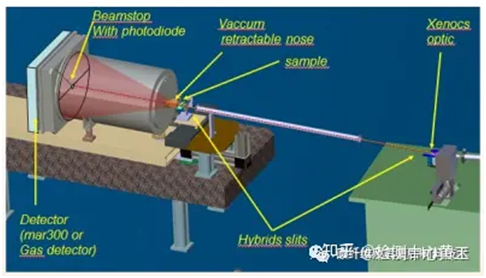
2023-11-13 10:00X-ray diffractometer is a device that uses the principle of interaction between X-rays and substances to obtain information such as crystal structure and lattice constant of substances by measuring the diffraction Angle and intensity of X-rays in substances. SAXS has no specific requirements for the form of the sample, block, powder and liquid are acceptable, but requires that the structure of interest has an electron density fluctuation with the surrounding environment, known as contrast.
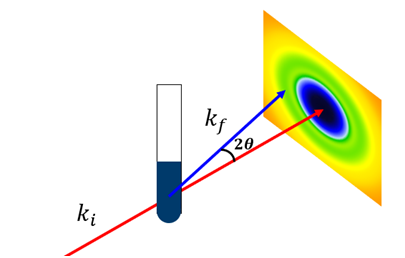
Small Angle X-ray scattering is widely used in many fields, including materials science, biomedicine, environmental science and so on. For example, in materials science, small-angle X-ray scattering is used to study the crystal structure of polymers. By measuring the small Angle X-ray scattering pattern of polymer samples, we can know the crystal structure, lattice constant and disorder of polymer.
In biomedicine, we can use small-angle X-ray scattering to study the structure and function of proteins. Small Angle X-ray scattering can be used to study the structure and function of insulin. By measuring the small Angle X-ray scattering pattern of insulin samples, we can know the crystal structure and disorder of insulin.
Overall, small-angle X-ray scattering is an important analytical tool that can help us gain insight into the microstructure and properties of matter. With the development of science and technology, the application of small Angle X-ray scattering will be more extensive.
