- Home
- >
News
X-ray diffractometer (XRD) can be divided into X-ray powder diffractometer and X-ray single crystal diffractometer, the basic physical principle of the two is the same.
XRD is a means of research which is Diffraction by X-Ray diffraction of a material to analyze its diffraction pattern to obtain information such as the composition of the material, the structure or shape of atoms or molecules inside the material.
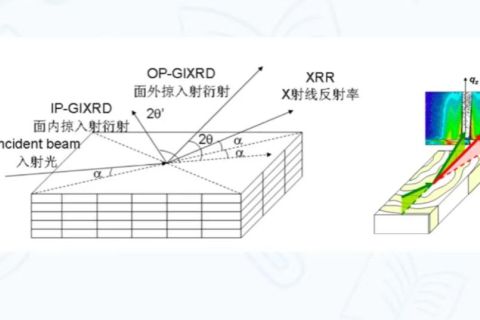
Grazing-incidence X-ray diffraction (GI-XRD) is a kind of X-ray diffraction technique, which is different from the traditional XRD experiment, mainly by changing the Angle of X-ray incidence and the orientation of the sample.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is currently a powerful method for studying crystal structure (such as the type and location distribution of atoms or ions and their groups, cell shape and size, etc.).
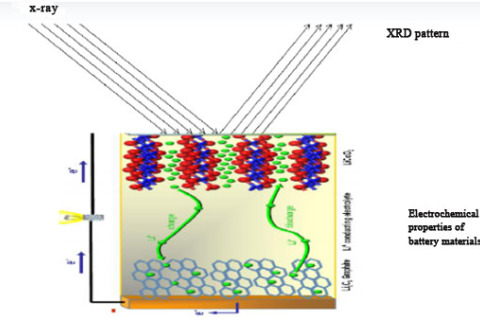
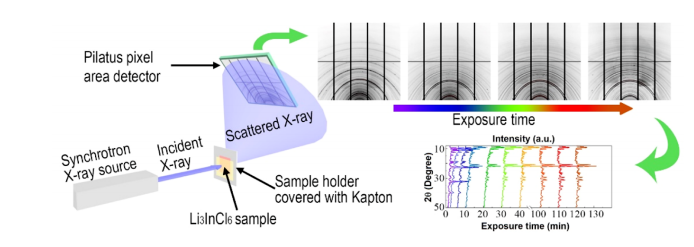
Based on Bragg's Law, in-situ X-ray diffraction (XRD) can be used to monitor the change of phase and its lattice parameters in the electrode or electrode-electrolyte interface in real time during the charge-discharge cycle of a battery.
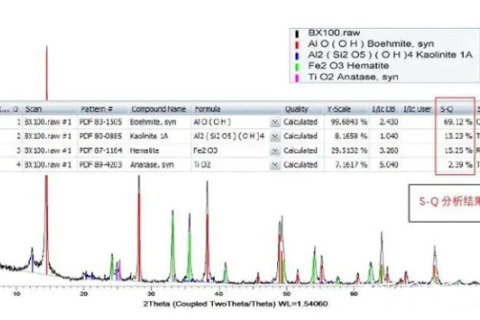
X-ray diffractometer is mainly used for phase characterization, quantitative analysis, crystal structure analysis, material structure analysis, crystal orientation analysis of powder, block or thin film samples.
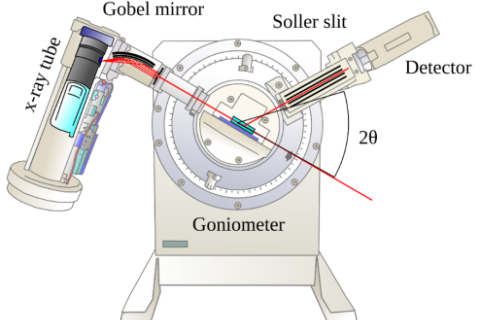
X-ray diffractometer , also known as X-ray crystal diffractometer, abbreviated XPD or XRD, is an instrument to study the internal microstructure of matter. X-ray diffractometer has the advantages of high precision, high stability and convenient operation.
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) is a major method for studying the phase and crystal structure of a substance. When a substance (crystal or non-crystal) is diffraction analysis, the substance is irradiated by X-rays to produce different degrees of diffraction phenomenon, material composition, crystal type, intramolecular bonding mode, molecular configuration, conformation and other material characteristics determine the specific diffraction pattern of the substance.