- Home
- >
News
XAFS, as an advanced characterization technique for the local structure analysis of materials, can provide more accurate atomic structure coordination information in the short-range structure range than X-ray crystal diffraction.
A material whose properties are dominated by two-dimensional effects, the properties of the material on a two-dimensional scale are different from its properties on a larger scale.
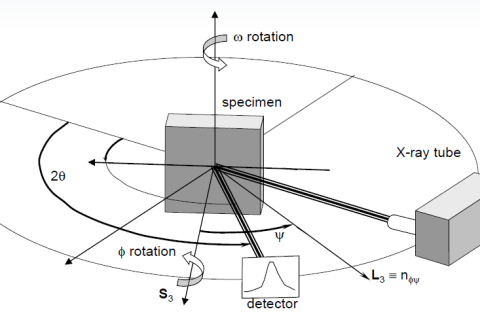
Residual stress has a great impact on the dimensional stability, stress corrosion resistance, fatigue strength, phase change and other properties of materials and components. Its measurement has been widely concerned by academia and industry.
XRD technology plays an important role in the research and development of ceramic materials. It provides a reliable scientific basis for the synthesis, preparation process optimization, performance improvement and application popularization of ceramic materials.
It is difficult to quantify the amorphous and crystalline phases of cement materials due to the complexity of the mineral phases in the mixture and the significant overlapping peaks. Excellent results can be obtained by Rietveld refinement of the measured sample using standard measurement configurations.
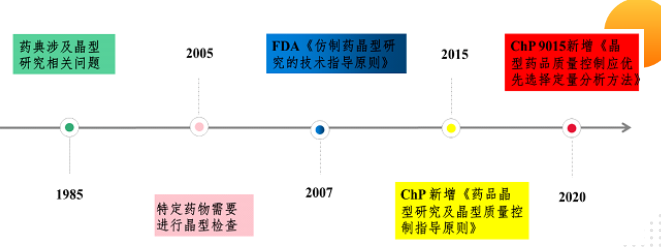
Powder X-ray diffraction, as one of the methods for the study of drug polymorphism, has the advantages of not destroying samples and simple operation, and is the main method for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of drug polymorphism at present.
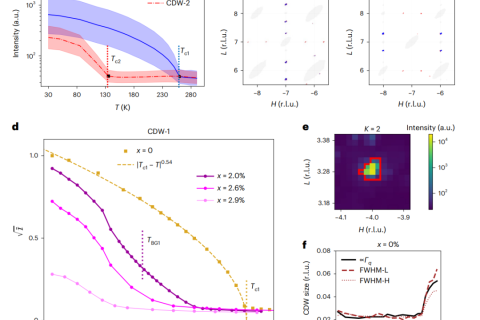
The Bragg glass phase is a near-perfect crystalline phase with glassy characteristics that is expected to occur in vortex lattices and charge density wave systems in the presence of disorder.
This paper introduces the related knowledge of crystal pattern and crystal fetish
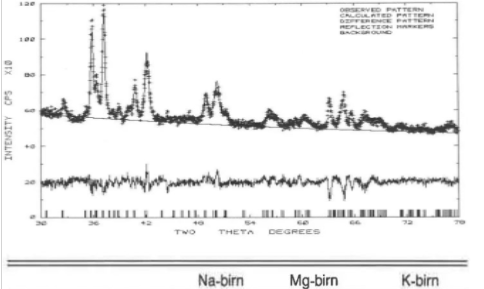
X-ray diffraction technique is widely used in drug analysis. X-ray diffraction technique is an analytical method used to study the structure of a substance. This technique has many applications in drug analysis.