- Home
- >
News
X-ray technology plays a vital role in medical and scientific research, and recent advances in X-ray technology are enabling brighter, stronger beams and imaging of increasingly complex systems under real-world conditions.
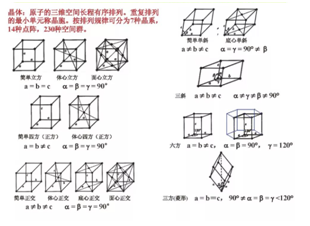
The three-dimensional space of atoms is arranged in a long-range order, and the smallest unit of repeated arrangement is called the cell, which can be divided into 7 kinds of crystal systems, 14 kinds of lattice, and 230 kinds of space groups according to the arrangement law.
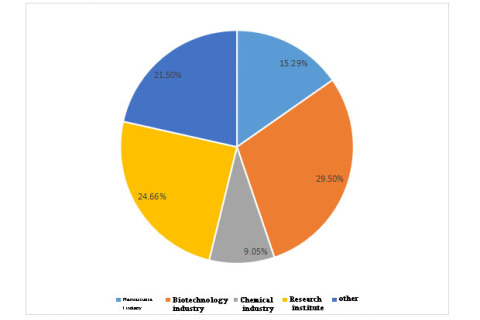
Dandong Tongda TD-5000X-ray single crystal diffractometer won the "ACCSI2023 Instrument and Detection 3i Award --2022 Annual Scientific Instrument Industry Outstanding New Product Award".
Crystals, although long admired for their regularity and symmetry, were not studied scientifically until the 17th century. Let's take a look at the early history of crystallography.
Using the principle of X-ray diffraction, the cutting Angle of natural and artificial single crystals is accurately and quickly determined, and the cutting machine is equipped for directional cutting of the said crystals.
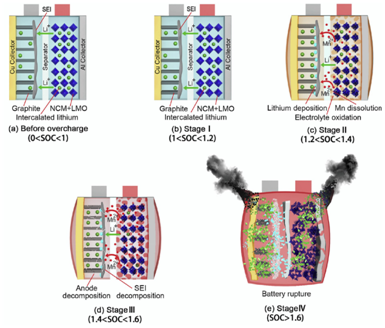
X-ray diffraction technology is widely used in the research of lithium-ion batteries. XRD is a conventional method for qualitative and quantitative analysis of phases in materials.
The Mid-Autumn Festival, the festival celebration! Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. for all employees to issue Mid-Autumn Festival benefits!
Global X-ray diffractometer (XRD) has developed steadily in recent years, and China is a market with great development prospects.
The application of new technologies and new products such as 5G, big data, and artificial intelligence will bring a huge semiconductor market demand, and global semiconductor equipment spending has entered an upward cycle.
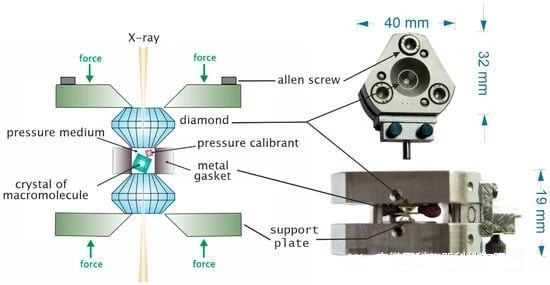
In recent years, there has been a growing interest in the measurement of high-pressure biological samples. This is reflected in the development of new techniques for pressure measurement that are different from those implemented by DAC. One of them is the technique of freezing crystals under pressure.