News
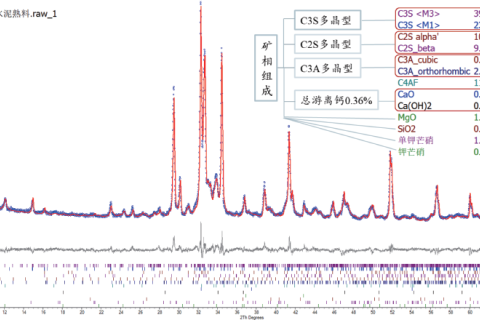
X-ray diffractometer is a kind of instrument to analyze the crystal structure, phase composition and crystal orientation of a substance by the interaction of X-ray with matter.
The properties of materials are often determined by their phase composition, and XRD is widely used as one of the main means of phase analysis.
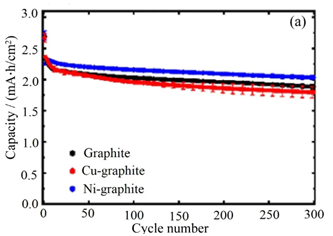
The degree of graphitization refers to how closely the crystal structure of the graphite material resembles perfect graphite after rearranging the amorphous carbon structure.
On the occasion of the Dragon Boat Festival, all staff of Dandong Tongda wish you a happy holiday!
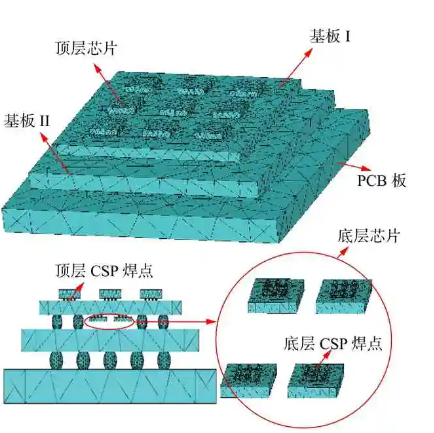
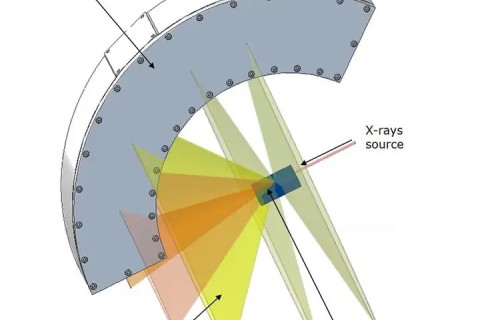
An X-ray stress diffractometer is a widely utilized instrument in the field of materials science and engineering for measuring the internal stress distribution of materials.
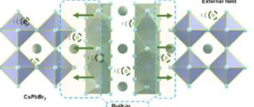
A research team from the Hefei Institute of Physical Sciences at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has recently conducted a study proposing a novel method to improve X-ray detection by incorporating out-of-phase CsPb2Br5 peritectic crystals into CsPbBr3 block materials.
XRD is the most advanced X-ray diffractometer system in the world today, with precise design and complete functions, and can flexibly adapt to various microstructure determination such as powder.
Founded in 2002, Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. is a national high-tech enterprise with X-ray analysis instruments and X-ray non-destructive testing instruments as its leading products
Recently, the Ministry of Science and Technology announced the list of the second batch of key projects under the 2023 National key research and Development Plan "Basic scientific research Conditions and major scientific instruments and equipment research and development".