News
X-ray diffractometer is mainly used for phase qualitative and quantitative analysis, bulk structure analysis, material structure analysis, crystal orientation analysis, macroscopic or microscopic stress determination, particle size determination, crystallinity determination, etc. of powder, block or film samples.
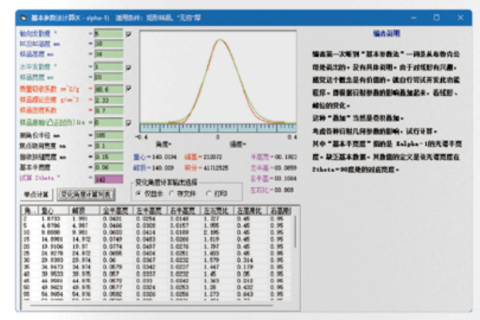
Software feature description:This program is a self-developed program. It contains various quantitative methods developed independently, in accordance with diffraction theory, and calculated entirely using integrated intensity.Analysis function. If this program contains the function of full spectrum peak fitting, separation and quantification that can still be accurately quantified under different phase line widths; as The function of the integrated intensity quantification method, which can conveniently automatically eliminate the interference of overlapping peaks of this phase and other phases, and is not affected by the different line widths of each phase, such as Complete PDF file calculation spectrum combination full spectrum fitting method, custom card file calculation spectrum combination full spectrum fitting method, etc. All the above methods use integration. The concept of intensity can be quantified by full spectrum fitting without involving structure and with different phase line widths. Can exclude overlapping peaks.Interference can reduce or eliminate the influence of preferred orientation.
Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. is a professional manufacturer of X-ray products, with two main series of products: X-ray analysis instruments and X-ray non-destructive testing instruments. And in 2013, it became the undertaking unit of the national major scientific instrument and equipment development special X-ray single crystal diffractometer project of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China. Our company adheres to the principles of customer first, product first, and service first, insists on people-oriented, and has a strong scientific and technological team. We are committed to providing users with the highest quality high-tech products with advanced technology, and providing strong support and services with efficient technical consulting and after-sales service institutions.
Excellent detector, polycrystalline sample X-ray diffraction analysis, precise instrument tuning, excellent resolution
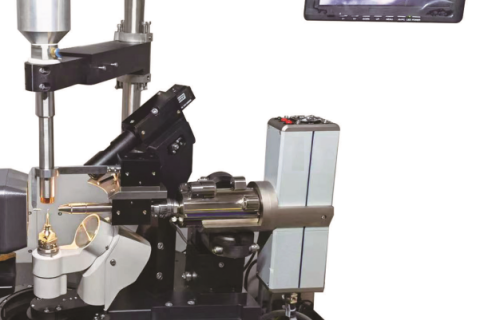
The use of four concentric circles technique ensures that the center of the angle measuring instrument remains unchanged regardless of any rotation, achieving the goal of obtaining the most accurate data and higher completeness. Four concentric circles are a necessary condition for conventional single crystal scanning.
θ - θ structure, the sample remains stationary while the radiation source and detector rotate; Adopting imported high-precision bearing transmission, with good stability; High precision fully closed-loop vector drive servo system control, Contains 32-bit RISC microprocessor and high-resolution magnetic encoder for automatic error correction;
Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. is a professional enterprise that produces X-ray products. Its main product is X-ray analysis instruments, and in 2013, it became the project undertaker for the National Major Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Special X-ray Single Crystal Diffraction Instrument of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China. Our company adheres to the principles of customer first, product first, and service first, insists on people-oriented, and has a strong technology team. We are committed to providing users with the highest quality high-tech products with advanced technology, and providing strong support and services to users with efficient technical consulting and after-sales service institutions.
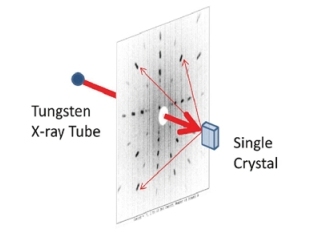
The X-ray single crystal diffractometer is mainly used to determine the three-dimensional spatial structure and electron cloud density of crystalline substances such as inorganic, organic, and metal complexes, and to analyze the structure of special materials such as twinning, non commensurate crystals, quasicrystals, etc. Determine the accurate three-dimensional space (including bond length, bond angle, configuration, conformation, and even bonding electron density) of new compound (crystalline) molecules and the actual arrangement of molecules in the lattice; It can provide information on the crystal cell parameters, space group, crystal molecular structure, intermolecular hydrogen bonding and weak interactions, as well as structural information such as molecular configuration and conformation. It is widely used in analytical research in chemical crystallography, molecular biology, pharmacology, mineralogy, and materials science.
Desktop X-ray diffractometer: mainly used for phase analysis of powders, solids, and similar paste materials. It utilizes the principle of X-ray diffraction to perform qualitative or quantitative analysis on polycrystalline materials such as powder samples and metal samples, as well as crystal structure analysis. It is widely used in industries such as industry, agriculture, national defense, pharmaceuticals, minerals, food safety, petroleum, education, and scientific research.
Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. is committed to the research and development, production, and sales of X-ray diffractometers. The company currently has X-ray diffractometers, X-ray desktop diffractometers, X-ray single crystal diffractometers, X-ray crystal analyzers, and other products, which are sold both domestically and internationally and have received unanimous praise from the industry.