
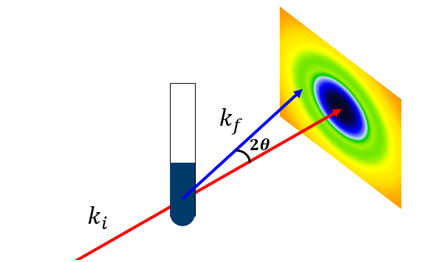
XRD- Small Angle X-ray scattering
2023-12-21 10:00Small Angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) is a technology that collects scattered signals generated by X-rays passing through a sample to study the structural information of a sample in the range of 1~100 nm.
Example:Since the shape and size of nanoparticles will have an impact on their physical and chemical properties, in order to achieve a more accurate analysis of the shape and size of nanoparticles, so as to better utilize nanoparticles, it is necessary to adopt a more statistically significant SAXS technology. First, TEM was used to conduct preliminary analysis of the morphology and size of the nanoparticles, and then SAXS data of different nanoparticle dispersions were collected, and different P-values were obtained by analyzing the data with different shape factors (i.e., cube, sphere, and superball). When p=1, the nanoparticle is spherical, and when, the nanoparticle is cube. The fitted P-values are shown in Figure 2(a).
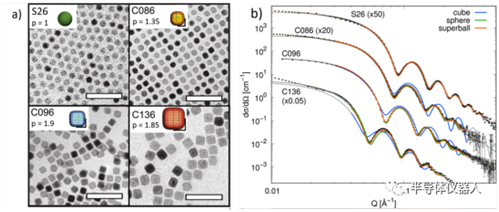
FIG. 2 (a) TEM images of four different shapes of nanoparticles and (b) SAXS data and fitting results.
