News
XRD is the most advanced X-ray diffractometer system in the world today, with precise design and complete functions, and can flexibly adapt to various microstructure determination such as powder.
Founded in 2002, Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. is a national high-tech enterprise with X-ray analysis instruments and X-ray non-destructive testing instruments as its leading products
Recently, the Ministry of Science and Technology announced the list of the second batch of key projects under the 2023 National key research and Development Plan "Basic scientific research Conditions and major scientific instruments and equipment research and development".
Different crystal forms of the same drug may differ significantly in appearance, solubility, melting point, etc., affecting the stability, production, bioavailability, and safety of the drug.
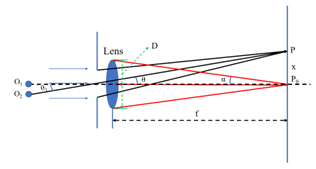
XRD is a research method to obtain information such as the composition of the material, molecules inside the material by X-ray diffraction and analysis of its diffraction pattern.
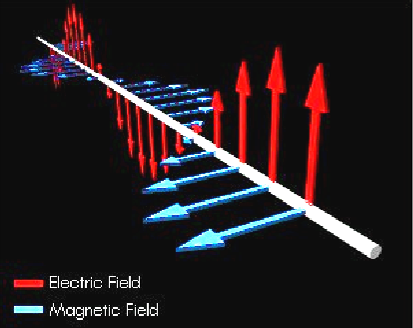
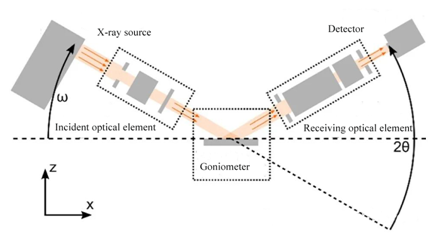
X-ray diffraction is a method to study the phase and crystal structure of a substance by using the diffraction phenomenon of X-rays in a crystal.
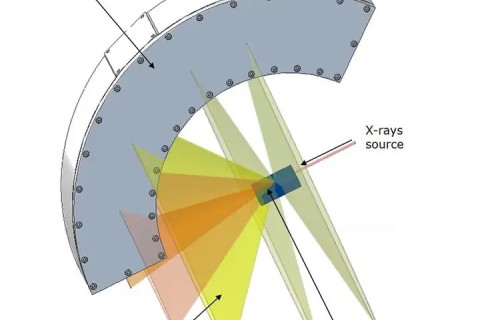
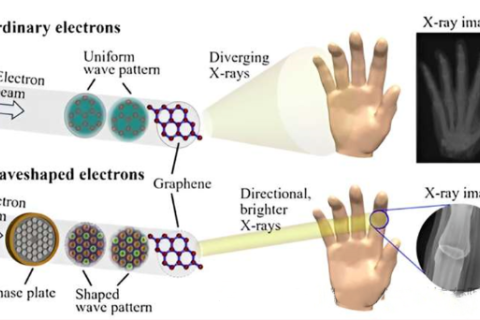
Scientists led by NTU Singapore have developed and simulated a new energy-saving method that can produce highly focused and finely controlled X-rays that are a thousand times stronger than conventional methods.
X-ray diffraction technique is often used to detect the crystal quality of wafers and epitaxial wafers.
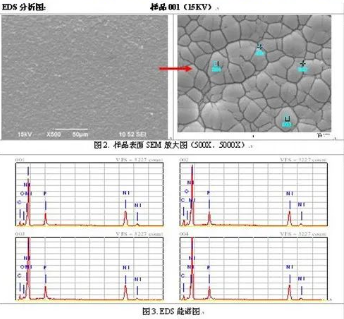
XRD analysis is a method to analyze the structure of the internal atoms in the space distribution of substances by using the X-ray diffraction formed by crystals.