News
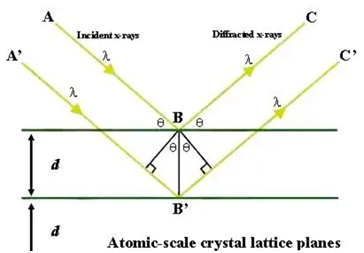
X-ray diffraction is a method of analyzing the structure or composition of a sample by shining a monochromatic X-ray beam on it.
XRD technology provides a powerful tool for studying the chemical composition and mineral composition of brine. Through the use of this technique, the characteristics and value of brine can be more fully understood.
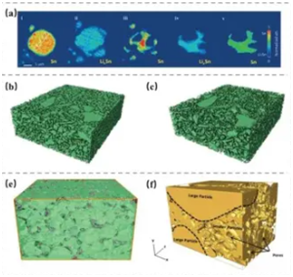
NREL researchers have utilized state-of-the-art X-ray diagnostic capabilities as a nondestructive method to examine the composition and structure of battery materials.
Battery material analysis helps to understand and optimize battery performance, improve battery safety and life, reduce costs, and promote the development and application of new materials.
XRD qualitative detection is convenient, fast and less interference. With the continuous innovation of technical means, X-ray diffraction technology has a broader application prospect in the field of material analysis.
XRD uses monochromatic X-rays as the diffraction source, which can generally penetrate the solid, so as to verify its internal structure. XRD gives the bulk phase structure information of the material.
Since the 1990s, synchrotron radiation X-ray tomography imaging technology has been widely used in materials research.
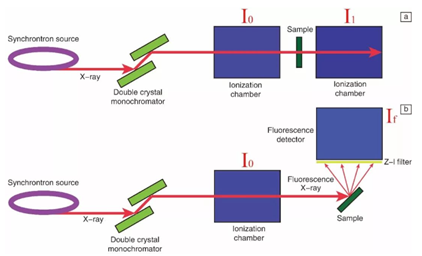
X-ray absorption spectroscopy is a spectral technique to analyze the elemental composition and electronic states of materials by using the signal changes before and after the incident of synchrotron radiation X-rays.
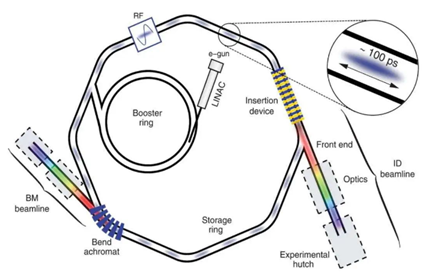
Synchrotron radiation is the electromagnetic radiation produced along the tangent direction of the orbit when the electron is moving in high-speed curve, which can be used to carry out many advanced scientific and technological research.