- Home
- >
News
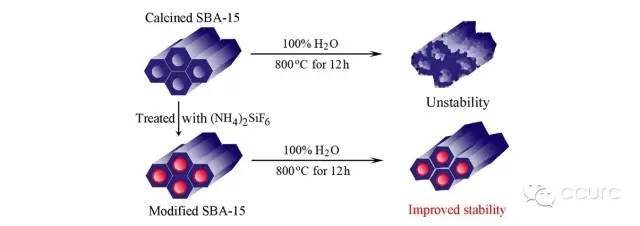
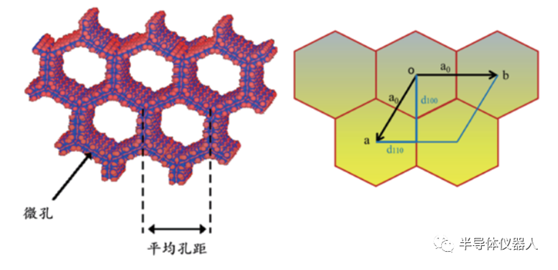
SBA-15 is a kind of mesoporous molecular sieve, and its synthesis is another important chemical technology emerging in recent years.
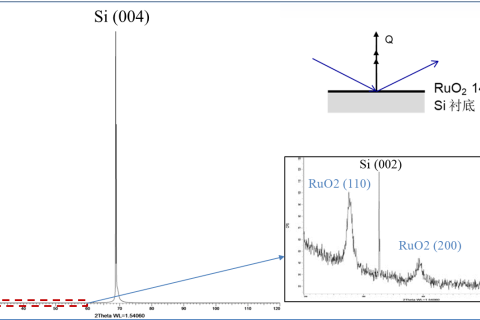
Grazing incidence means that the X-ray is exposed to the film at a very small incidence Angle (< 5°), which greatly reduces the penetration depth in the film.At the same time, the low incidence Angle increases the irradiation area of the X-ray on the sample
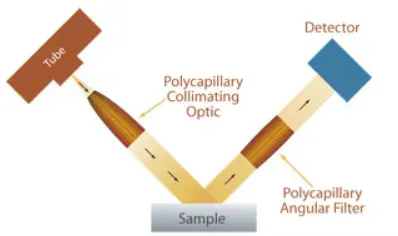
Parallel beam XRD of X-ray optical crystals has been successfully applied in thin film analysis, sample texture evaluation, crystal phase and structure monitoring, etc.
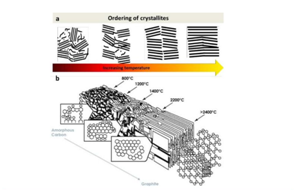
Micro-ct technology has significant advantages in the characterization of ceramics, which can reveal the composite structure inside the material without damage, and restore the key technology in the production of ceramics.
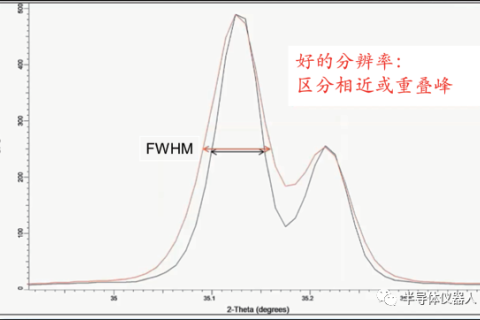
As one of the important means of material structure characterization, XRD is widely used in materials, physics, chemistry, medicine and other fields.
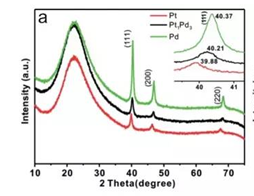
X-ray diffractometer is mainly used for phase characterization, quantitative analysis, crystal structure analysis, material structure analysis, crystal orientation analysis of powder, block or thin film samples, etc.
XRD as a qualitative analysis means is not blind, with the help of analysis software just for convenience, fundamentally speaking, the most important thing is the XRD pattern itself.
As a new material characterization technology, PDF (Pair Distribution Function) is useful in the study of the local structure of both crystal and amorphous materials.
The structural stability of SBA-15 is closely related to its pore size and properties, and XRD is one of the effective methods to characterize its structure.
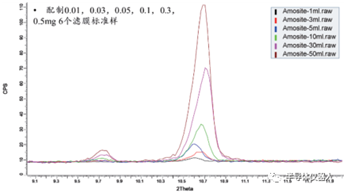
To determine whether there is asbestos in talc is usually a combination of polarizing or electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction, and the quantitative analysis of asbestos mainly uses X-ray diffraction method.
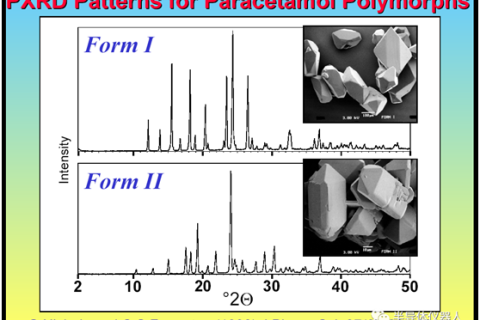
Most drugs exist in the form of crystals, using X-ray diffraction, we can obtain the diffraction information of drug characteristics for each different crystal type.
Dandong Tongda Technology Co., LTD., with professional technology and perfect service, has won the trust of scientific research workers around the world.