
Application of XRD in petroleum industry
2023-09-21 10:00As a powerful tool for material analysis, XRD also has a wide range of applications in the petroleum industry: mineral and whole rock analysis, type and quantitative analysis of clay, catalyst characterization, scaling and corrosion product analysis. This paper introduces how to use Bruker D2 Phaser X-ray diffractometer for qualitative phase and quantitative analysis of sedimentary scale.
1. Introduction to scaling:
Scaling is a solid deposit in a solution or suspension. The conditions for scale formation are complex and are determined by a range of variables, including dissolved gas, type and concentration of ions, temperature, pressure, PH, and salinity.
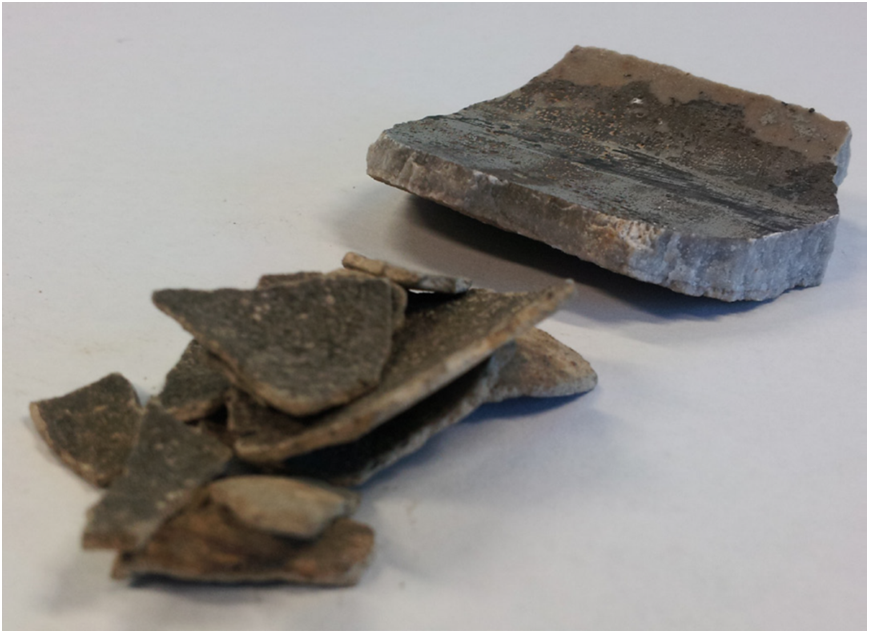
From a production perspective, scaling and fouling is an important issue for the oil industry, as these deposits can lead to a rapid decline in the flow of oil pipelines and clogging of valves and drilling ports. Figure 1 shows two different thicknesses of deposition scaling, both of which result in reduced pipeline capacity.

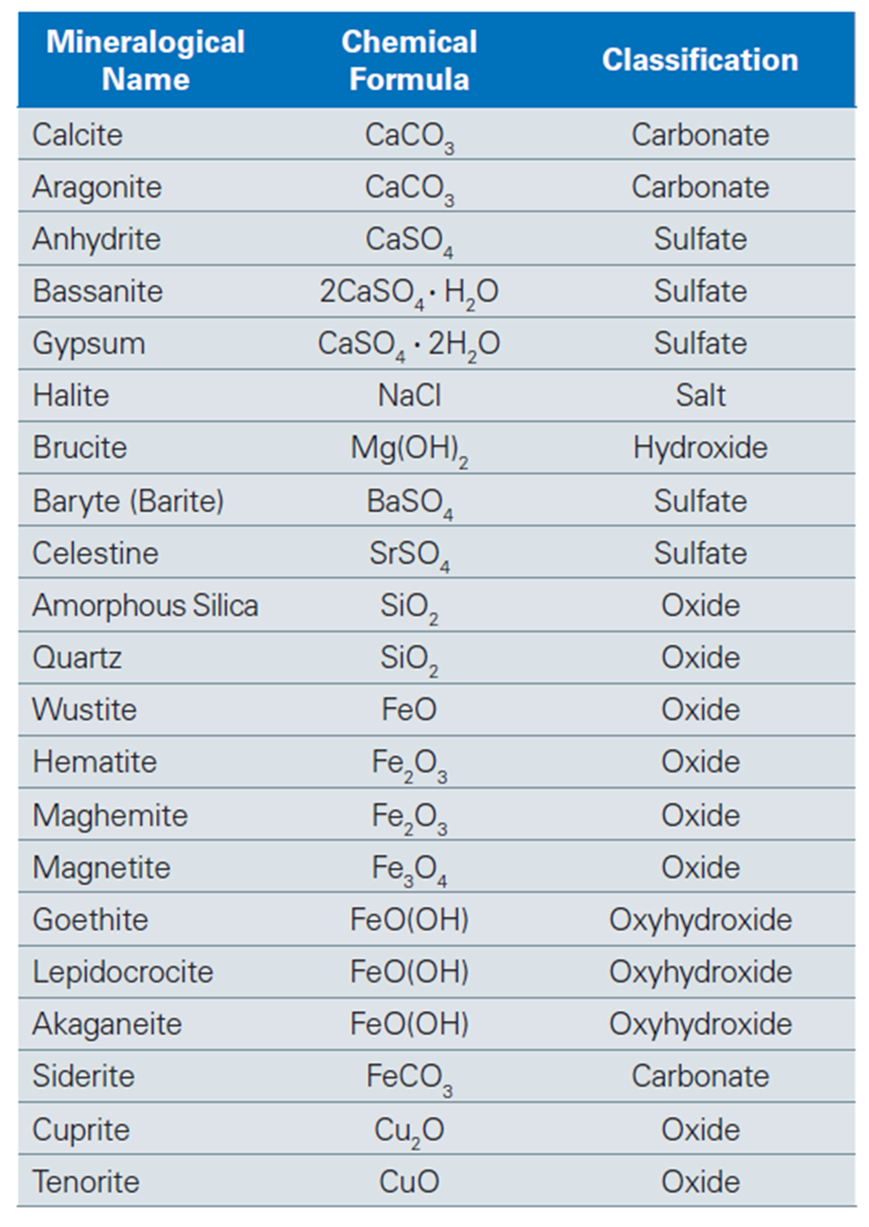
Some representative industrial scale and corrosion products, such as calcium carbonate and barium sulfate, are listed in Table 1. The phase of scale formation is often related to the formation conditions and the place of origin.
For deposited scale or corrosion products, the ultimate goal of characterizing them is to develop a reasonable treatment process to remove or prevent their production, thereby reducing maintenance costs and time. In this report, the sedimentary structure samples were qualitatively and quantitatively analyzed by X-ray diffraction method.
2. Experimental part
First, the collected samples are crushed into coarser particles, which are then ground in an agate mortar to a fine powder of less than 325 mesh. If the sample volume is large, it can be treated with mechanical grinding equipment such as mill or vibration mill. Sample analysis can be done using a bench powder diffractometer.

3. Experimental results
There are many types of deposited scaling materials, and it is important to determine the phase composition of each sample, determine the cause of deposition, and propose treatment options or prevent its formation. The treatment methods of root deposit scaling are: (1) acid liquid treatment; (2) binding ions by chelation; (3) Physical methods such as water flushing or grinding.
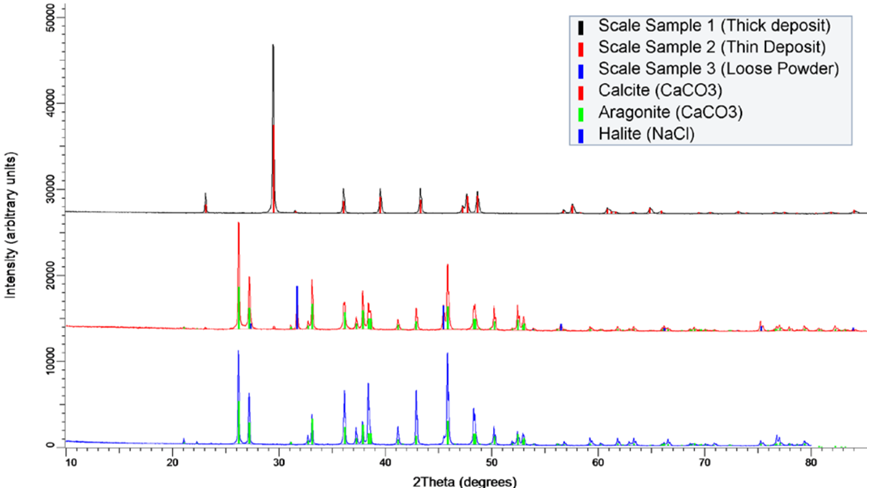
The polycrystalline form of calcium carbonate is taken as an example to illustrate the above contents. CaCO3 has two crystal forms, calcite and aragonite, which are formed in different local environments.
The diffraction patterns of several calcium-containing sediment samples are shown in Figure 3. After understanding the phase composition, the formation mechanism of sedimentary scaling can be analyzed, and targeted treatment methods can be further developed.
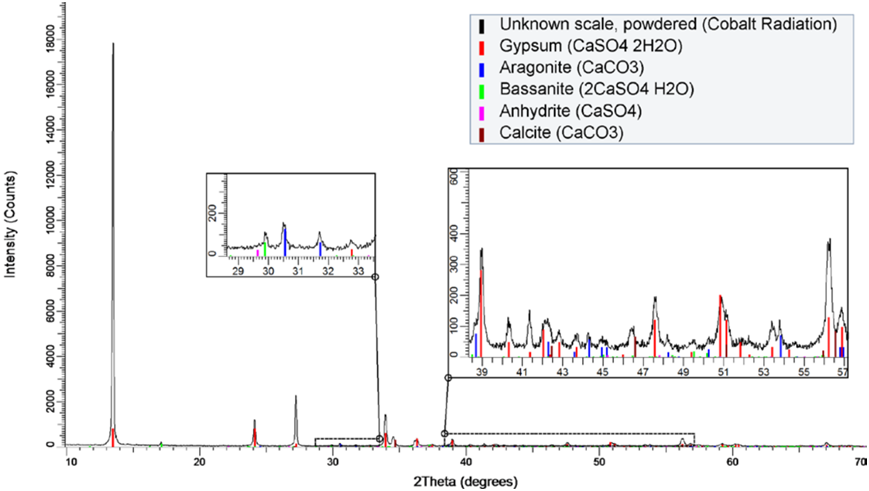
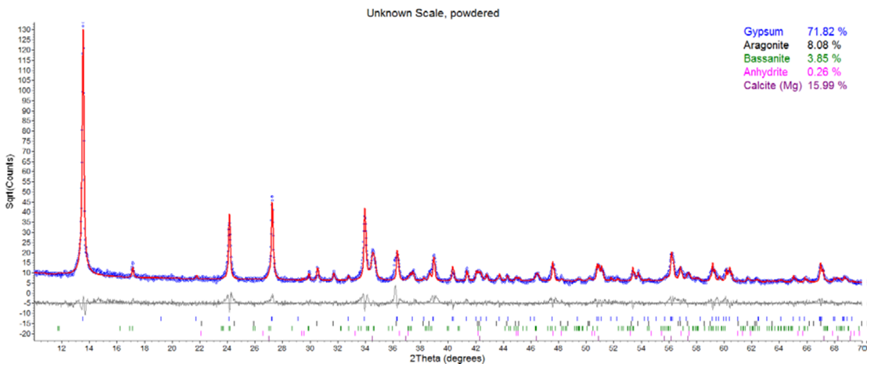
For a mixture of multiple phases, the amount of each phase can be determined by the structure of each mineral composition, as shown in Figure 4 (a sample of a sediment containing mainly calcium sulfate). The relative mass percentage of each phase is shown in Figure 5.
4. Conclusion
XRD is a powerful tool for qualitative and quantitative phase analysis of industrial sediments and corrosion products. X-ray diffraction is often used as an auxiliary means of elemental analysis to provide a more detailed characterization of material analysis, especially to distinguish phases with similar chemical composition, so XRD is widely used in the petroleum industry.
