- Home
- >
News
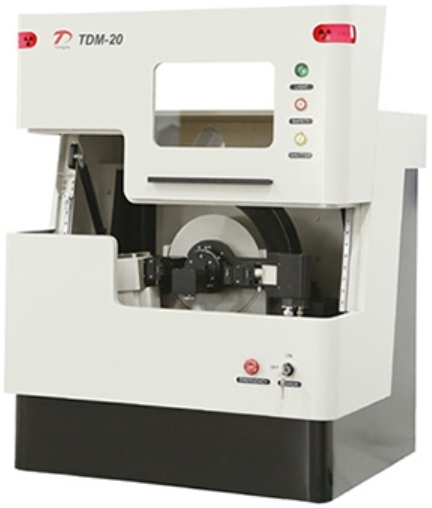
The TDM-20 benchtop XRD redefines performance standards with a groundbreaking 1200W power core—double the mainstream level. This enables faster, more precise analysis from R&D to QC in pharmaceuticals, materials science, mining, and food safety.
The Diffractometer X-Ray Tube manufactured by Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. serves as a core component in numerous X-ray analytical instruments within China. Dandong Tongda's Diffractometer X-Ray Tube primarily features the following technical characteristics: Diverse Target Material Options: This X-ray tube offers a variety of target material choices, including Cu, Co, Fe, Cr, Mo, Ti, W, and more. Users can select the most suitable target material based on the elemental composition of the material being tested and the specific analysis requirements, to achieve optimal analytical results. Flexible Focal Spot Configurations: The product provides different focal spot sizes, such as 0.2×12mm, 0.4×14mm (fine focus), and 1×10mm. Smaller focal spot sizes help improve spatial resolution, while the different shape designs meet the optical system requirements of various analytical instruments like XRD and XRF. Wide Power Range: The maximum output power of the X-ray tube covers multiple levels, including 2.0kW, 2.4kW, and 2.7kW, enabling it to adapt to various application scenarios from routine analysis to those requiring high power. Key Technologies and Performance Advanced Generator Technology: The high-frequency, high-voltage generator designed for use with the X-ray tube can achieve a maximum output power of 5kW. It utilizes microcomputer automatic control, with tube voltage adjustment precision up to 1kV per step and tube current adjustment precision up to 1mA per step, ensuring precise and stable output signals. Exceptional Stability Performance: The output stability of the generator is better than 0.01%. The comprehensive stability of some high-end models can even reach ≤0.3%. This high level of stability is crucial for precision analytical work that requires long-term data acquisition. Comprehensive Safety Protection: The equipment is equipped with extensive alarm and protection devices, including multiple protection functions such as over-voltage, over-current, over-power, water shortage, and X-ray tube over-temperature, ensuring safe and reliable operation. Main Application Areas Dandong Tongda's X-ray tubes are primarily used in the following types of analytical instruments: X-Ray Diffractometers (XRD): Used for phase analysis of materials, crystal structure determination, etc. X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometers (XRF): Used for qualitative and quantitative elemental analysis. Crystal Analyzers and Orienters: Can be used for single crystal orientation, defect inspection, etc.
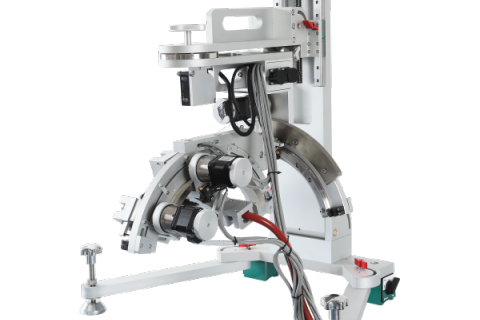
Fiber Accessories utilize the X-ray diffraction (transmission) method to analyze the unique crystal structure of fibers. Parameters such as crystallinity and full width at half maximum (FWHM) are used to determine the orientation degree of the sample. Main Functions and Features of Fiber Accessories: Maintaining Fiber Orientation: This is the most critical aspect. Fibers typically exhibit high anisotropy, with crystals preferentially aligned along the fiber axis. Fiber Accessories can straighten and secure fiber bundles, preserving their original orientation to measure orientation degree and distribution. Adapting to Different Sample Forms: Single Fiber: Extremely thin, requiring special clamps or frames for fixation. Fiber Bundle: Multiple fibers arranged in parallel; Fiber Accessories must align and tension them uniformly. Fiber Fabric: Materials like cloth require a flat frame to stretch them taut. Enabling Special Testing Modes: Transmission Mode: Suitable for thin fiber bundles or single fibers. Fiber Accessories include a dedicated frame to tension the fiber, allowing X-rays to penetrate the sample directly. Reflection Mode: Used for thicker fiber bundles or fabrics. Fiber Accessories provide a flat sample surface for this mode. Fiber Sample Holder: This is a simple metal or plastic frame equipped with slots or knobs. During operation, both ends of the fiber bundle are fixed to the holder, and knobs are rotated to tension the fiber, keeping it straight and parallel. The entire holder can be placed in the XRD goniometer for testing, similar to a standard sample. In summary, Fiber Accessories for XRD are specialized sample fixation devices designed for testing fibrous samples with anisotropic structures. Their core function is to maintain and regulate fiber orientation, while advanced versions may support in-situ stretching and other functionalities, providing critical insights into the orientation of crystal structures in fibers.
The multi-functional residual stress analyzer developed by Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. is designed to meet the needs of fast and accurate measurements in both laboratory and field environments. Based primarily on the X-ray diffraction principle, it enables non-destructive testing of the residual stress state inside materials. Versatile All-in-One Analysis This analyzer integrates multiple material analysis functions, significantly enhancing equipment utility and efficiency: Residual Stress Analysis: Supports various measurement modes such as standard同倾法 (omega-inclination), standard侧倾法 (psi-inclination), and standard摇摆法 (oscillation), capable of determining principal stresses and shear stresses for a comprehensive stress state evaluation. Retained Austenite Analysis: Employs the four-peak method for retained austenite testing, with fully automated data calculation for quick results. Diffraction Phase Analysis: Used to analyze crystal structures, chemical composition content, and distribution, helping researchers gain deeper insights into material constitution. Grain Size Analysis: Supports grain size evaluation from nanoscale to sub-micron scale, particularly suitable for fine grains ≤200 nm. Technical Features and Performance This instrument boasts multiple technical features aimed at ensuring precision, stability, and ease of use: High-Precision Measurement and Control: Utilizes a high-precision fully closed-loop vector drive servo system to ensure measurement accuracy and repeatability. Efficient Data Acquisition: Equipped with a multi-channel silicon strip linear array detector, which provides noise-free performance, high-intensity measurement, and rapid data collection to enhance detection efficiency. Portable Design: Features a lightweight construction, making it suitable not only for laboratory environments but also for on-site rapid measurements, adapting to various testing scenarios. User-Friendly Operation: Integrates Windows OS or automation functions, supporting one-click testing and real-time result display, lowering the operational barrier. Modularity and Safety: Employs a PLC control system with modular design for ease of operation and stable performance. Safety-wise, its low-power X-ray design complies with relevant safety standards, with radiation levels significantly below the annual public dose limit. Broad Application Fields Dandong Tongda’s multi-functional residual stress analyzer has extensive applications, covering almost all industrial sectors and research institutions requiring evaluation of material mechanical properties: Manufacturing Quality Control: Used to detect residual stresses in stamped, cast, and rolled parts during processing. Automotive Industry: Tests residual stresses in critical components such as camshafts and connecting rods to ensure reliability and durability. Aerospace: Evaluates working loads in critical areas of aerospace materials to assess safety. Materials Science Research: Applicable to various metal materials (e.g., carbon steel, alloy steel, titanium alloy, nickel-based materials), glass, and composite materials for residual stress, retained austenite, phase, and grain size analysis. Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd.’s multi-functional residual stress analyzer demonstrates the company’s technical expertise in the field of material testing by integrating multiple analytical functions. This instrument provides engineers and researchers with a window into the intrinsic stress state of materials, helping to control product quality at the source, optimize process parameters, and thereby enhance product reliability and durability.
The TDM-20 X-ray Diffractometer (Benchtop XRD) is primarily used for phase analysis of powders, solids, and paste-like substances. Based on the principle of X-ray diffraction, it enables qualitative and quantitative analysis, as well as crystal structure analysis, of polycrystalline materials like powdered samples and metal samples. It is widely applied in industries including industry, agriculture, national defense, pharmaceuticals, mineralogy, food safety, petroleum, and education/research. Core Principle: X-ray Diffraction, the Key to the Microscopic World The TDM-20 X-ray Diffractometer operates on the principle of X-ray diffraction. When X-rays illuminate a sample, they interact with the atoms in the sample and diffract. Different crystal structures produce unique diffraction patterns, much like individual fingerprints. By analyzing these patterns, the instrument precisely reveals key information about the sample's crystal structure, phase composition, and more, uncovering the secrets hidden at the microscopic level. Performance Breakthrough The TDM-20 X-ray Diffractometer (Benchtop XRD) surpasses the previous international standard of 600W, undergoing a comprehensive upgrade to 1200W. The instrument features simple operation, stable performance, and low energy consumption. It can be equipped with either a proportional detector or a new high-speed array detector, resulting in a significant leap in overall performance. Device Features Compact size and lightweight design High-frequency, high-voltage power supply design for lower overall energy consumption Supports rapid sample calibration and testing Simplified circuit control for easy debugging and installation Full-spectrum diffraction angle linear accuracy reaches ±0.01° Rich Accessories The TDM-20 can be paired with various accessories, including a 1D array detector, proportional detector, 6-position automatic sample changer, rotating sample stage, among others. Conclusion The TDM-20 X-ray Diffractometer (Benchtop XRD) , with its outstanding performance, user-friendly operation, and broad range of applications, has become an indispensable tool across numerous industries and research fields. It acts like a "detective" of the microscopic world, helping us unravel the mysteries of material structure and driving progress in various domains. If you too seek to delve deeper into the microscopic secrets of matter, consider the TDM-20 to embark on a journey of precise and efficient research and production.
The TDM-20 high-power X-ray diffractometer(Benchtop XRD)is mainly used for phase analysis of powders, solids, and similar paste materials. The principle of X-ray diffraction can be used for qualitative or quantitative analysis, crystal structure analysis, and other polycrystalline materials such as powder samples and metal samples. Benchtop XRD is widely used in industries such as industry, agriculture, national defense, pharmaceuticals, minerals, food safety, petroleum, education, and scientific research. 1、Core features of TDM-20 benchtop X-ray diffractometer(Benchtop XRD): The loading of the new high-performance array detector has greatly improved the overall performance of the device, with a small size and light weight; The whole machine is integrated into the desktop size (usually ≤ 1m³), saving space and suitable for small laboratories or teaching environments;The working power of high-frequency and high-voltage power supply can reach 1600W; Quick analysis, able to calibrate and test samples quickly; By using high-performance detectors (such as two-dimensional detectors) and optimizing the optical path, sample scanning can be completed in a few minutes; Simple circuit control, easy to debug and install; The angle repeatability can reach 0.0001; Low power consumption and safety, using low-power X-ray tubes (such as ≤ 50W), equipped with multiple radiation protection, no need for special shielding rooms; User friendly, equipped with automation software, supporting one click operation, real-time data visualization, and standard database (such as ICDD PDF) comparison. 2. Typical application scenarios of TDM-20 benchtop X-ray diffractometer(Benchtop XRD): Materials Science of X-ray diffractometer(Benchtop XRD): Rapid identification of crystal structure and phase composition (such as metals, ceramics, polymers). Materials Science of X-ray diffractometer(Benchtop XRD): Industrial site testing of the crystal purity of raw materials or finished products (such as pharmaceuticals and battery materials). Materials Science of X-ray diffractometer(Benchtop XRD): Undergraduate experimental teaching, visually demonstrating the Bragg diffraction principle. Materials Science of X-ray diffractometer(Benchtop XRD): Mineral composition analysis of cultural relics or preliminary screening of field samples. 3.Technical parameters of TDM-20 benchtop X-ray diffractometer(Benchtop XRD): Project : parameter range X-ray source:Cu target (λ=1.54 Å), Mo target optional Voltage/current:10-50 kV/0.1-2 mA Angle measuring instrument range:0-90 ° 2θ (some models can be extended) Angle resolution:≤ 0.01 ° Detector type: one-dimensional linear or two-dimensional surface detector Sample size: Powder (milligrams), film or block 4.Advantages and limitations of TDM-20 benchtop X-ray diffractometer(Benchtop XRD): Advantages: Low cost (about 1/3-1/2 of large XRD), easy maintenance. Support non-destructive analysis and simple sample preparation (such as directly placing powder). limitations: The resolution and sensitivity are slightly lower than high-end devices, and may not be suitable for ultra-fine structural analysis. Extreme condition testing (such as high-temperature/high-pressure in-situ experiments) is usually not feasible.
The TDM-20 Benchtop X-ray diffractometer uses a new high-performance array detector, and the loading of this detector has greatly improved the overall performance of the machine. The TDM-20 Benchtop XRD is mainly used for phase analysis of powders, solids, and similar paste like materials. The TDM-20 Benchtop X-ray diffractometer utilizes the principle of X-ray diffraction to perform qualitative or quantitative analysis, crystal structure analysis, and other polycrystalline materials such as powder samples and metal samples. Benchtop XRD is widely used in industries such as industry, agriculture, national defense, pharmaceuticals, minerals, food safety, petroleum, education, and scientific research.
The TD-5000 X-ray single crystal diffractometer is mainly used to determine the three-dimensional spatial structure and electron cloud density of crystalline substances such as inorganic, organic, and metal complexes, and to analyze the structure of special materials such as twinning, non commensurate crystals, quasicrystals, etc. Determine the accurate three-dimensional space (including bond length, bond angle, configuration, conformation, and even bonding electron density) of new compound (crystalline) molecules and the actual arrangement of molecules in the lattice; It can provide information on the crystal cell parameters, space group, crystal molecular structure, intermolecular hydrogen bonding and weak interactions, as well as structural information such as molecular configuration and conformation. X-ray single crystal diffractometer is widely used in analytical research in chemical crystallography, molecular biology, pharmacology, mineralogy, and materials science. Single crystal XRD is a high-tech product under the National Major Scientific Instrument and Equipment Development Project of the Ministry of Science and Technology, led by Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd., filling the gap in the development and production of single crystal x-ray diffractometer in China.
XRD enables precise TiO2 phase quantification, crucial for product quality. Dandong Tongda's TD-series diffractometers, with specialized programs, ensure accurate rutile/anatase analysis (<0.2% error).
Dandong Tongda Science and Technology Co., Ltd. is an industry leader focused on R&D and innovation in key technologies like diffraction analysis. Through academia collaborations, it develops high-efficiency products with independent IP, breaking international monopolies. The company builds its brand on integrity and professionalism, adhering to "Excellence Sets the Standard, Integrity Builds the Brand" to enhance competitiveness and contribute to China's scientific instrument industry.
The TDM-20 high-power X-ray diffractometer (benchtop XRD) is mainly used for phase analysis of powders, solids, and similar paste like materials. The principle of X-ray diffraction can be used for qualitative or quantitative analysis, crystal structure analysis, and other polycrystalline materials such as powder samples and metal samples. It is widely used in industries such as industry, agriculture, national defense, pharmaceuticals, minerals, food safety, petroleum, education, and scientific research.
The TDM-20 X-ray diffractometer is mainly used for phase analysis of powders, solids, and similar paste like materials. The X-ray diffractometer can be used for qualitative or quantitative analysis, crystal structure analysis, and other polycrystalline materials such as powder samples and metal samples. X-ray diffractometer is widely used in industries such as industry, agriculture, national defense, pharmaceuticals, minerals, food safety, petroleum, education, and scientific research. Benchtop XRD is an experimental equipment used for analyzing the crystal structure of materials. Benchtop XRD determines the crystal structure, lattice parameters, and phase composition of the material by emitting X-rays and measuring the diffraction angle and intensity after their interaction with the sample.