- Home
- >
News
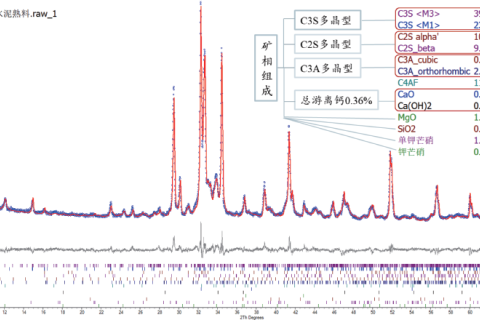
The properties of materials are often determined by their phase composition, and XRD is widely used as one of the main means of phase analysis.
The degree of graphitization refers to how closely the crystal structure of the graphite material resembles perfect graphite after rearranging the amorphous carbon structure.
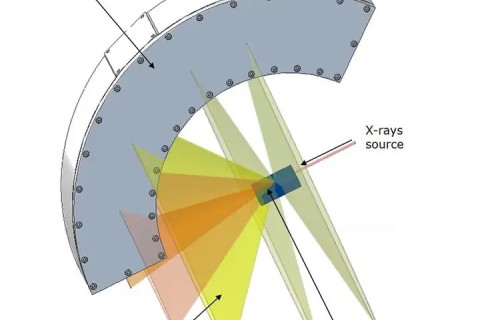
XRD is the most advanced X-ray diffractometer system in the world today, with precise design and complete functions, and can flexibly adapt to various microstructure determination such as powder.
Different crystal forms of the same drug may differ significantly in appearance, solubility, melting point, etc., affecting the stability, production, bioavailability, and safety of the drug.
XRD is a research method to obtain information such as the composition of the material, molecules inside the material by X-ray diffraction and analysis of its diffraction pattern.
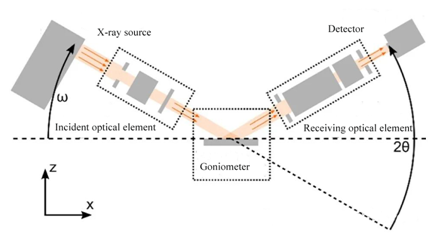
X-ray diffraction is a method to study the phase and crystal structure of a substance by using the diffraction phenomenon of X-rays in a crystal.
X-ray diffraction technique is often used to detect the crystal quality of wafers and epitaxial wafers.
XRD analysis is a method to analyze the structure of the internal atoms in the space distribution of substances by using the X-ray diffraction formed by crystals.
X-ray diffraction is a method of analyzing the structure or composition of a sample by shining a monochromatic X-ray beam on it.
XRD technology provides a powerful tool for studying the chemical composition and mineral composition of brine. Through the use of this technique, the characteristics and value of brine can be more fully understood.
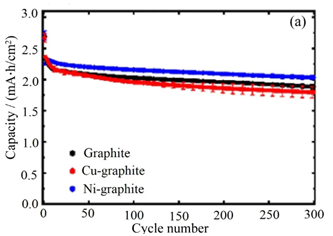
NREL researchers have utilized state-of-the-art X-ray diagnostic capabilities as a nondestructive method to examine the composition and structure of battery materials.