Degree of graphitization of negative electrode of lithium battery
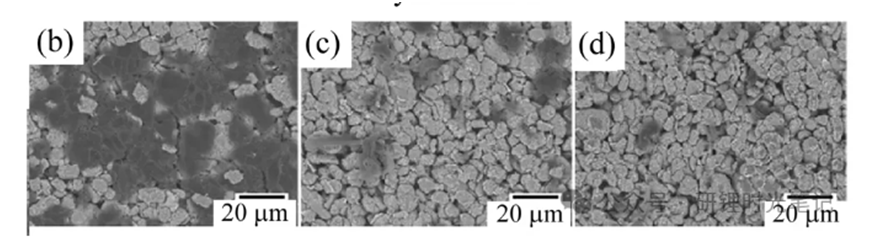
2024-06-12 00:00The degree of graphitization is a crucial parameter that quantifies the extent to which a carbon material undergoes structural rearrangement from amorphous carbon to approach perfect graphite. In the context of lithium-ion batteries, the degree of graphitization of graphite anode materials plays a pivotal role in determining battery performance.
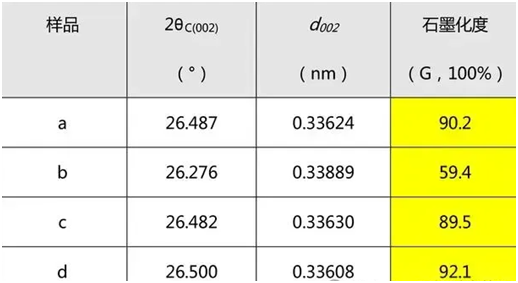
X-ray diffraction, a commonly used technique for determining the crystal structure of materials, is also highly effective in quantifying the degree of graphitization of graphite in lithium batteries. The degree of graphitization refers to how closely the crystal structure of the graphite material resembles perfect graphite after rearranging the amorphous carbon structure.
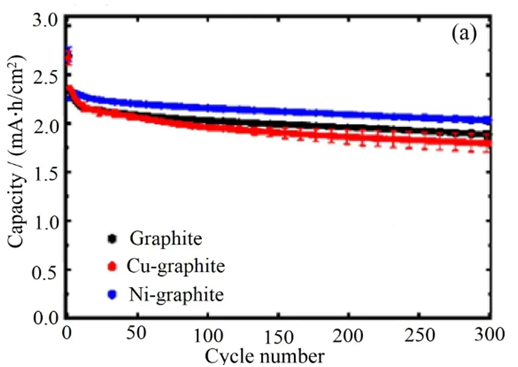
In X-ray diffraction measurements, when X-rays interact with a graphite crystal, they undergo scattering by the atoms and electrons within the crystal. The periodic arrangement of atoms in the crystal results in a fixed phase difference between these scattered waves, leading to spatial interference that strengthens some scattering directions while canceling others, thus giving rise to diffraction phenomena. The diffractometer automatically records the diffraction pattern of the sample and analyzes it to obtain information about the sample.