- Home
- >
News
X-ray diffraction technique is widely used in drug analysis. X-ray diffraction technique is an analytical method used to study the structure of a substance. This technique has many applications in drug analysis.
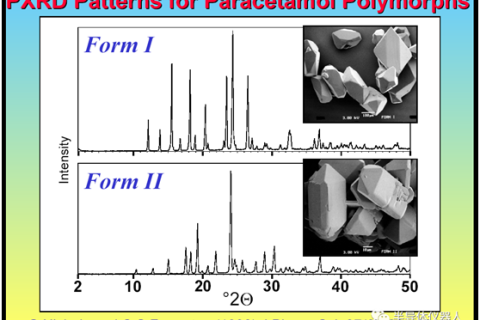
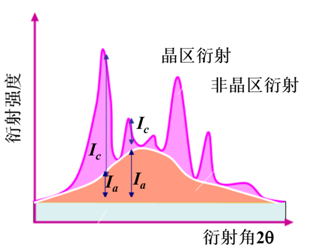
Powder X-ray diffraction, as one of the methods for the study of drug polymorphism, has the advantages of no sample destruction and simple operation.
X-ray diffraction spectroscopy mainly analyzes the crystal state and microstructure of materials, and there are two X-ray diffraction measurement methods for crystal analysis.
In the past 10 years, the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has used powder diffraction method to determine the crystal structure of many inorganic and organic compounds.
Parallel beam XRD of X-ray optical crystals has been successfully applied in thin film analysis, sample texture evaluation, crystal phase and structure monitoring, etc.
As one of the important means of material structure characterization, XRD is widely used in materials, physics, chemistry, medicine and other fields.
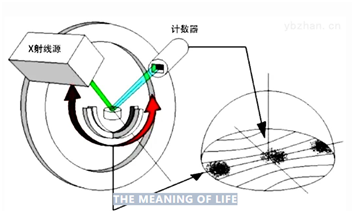
The full name of XRD is X-ray diffraction, which uses the diffraction phenomenon of X-ray in the crystal to obtain the X-ray signal characteristics after diffraction, and gets the diffraction pattern after processing.
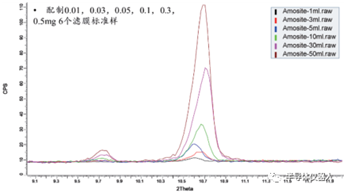
To determine whether there is asbestos in talc is usually a combination of polarizing or electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction, and the quantitative analysis of asbestos mainly uses X-ray diffraction method.
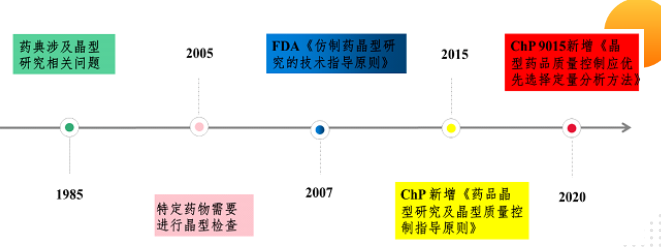
Most drugs exist in the form of crystals, using X-ray diffraction, we can obtain the diffraction information of drug characteristics for each different crystal type.
The Guiding Principle of Chiral Innovative drugs clearly stipulates that "the direct method for determination of molecular configuration of chiral drugs is single crystal X-ray structure analysis".
Unlike powder XRD, which is widely used in the late stage of drug development and production, single crystal X-ray diffraction technology plays an important role in the early and middle stages of drug development.
XRD technology is widely used in the fields of crystallography, physics and metallurgy, including qualitative and quantitative, crystal structure, mechanical analysis, etc. This paper mainly lists its application in polymer research.