
Knowledge of crystal diffraction
2023-10-14 10:001. Crystal lattice diffraction
For X-rays, the crystal is equivalent to a three-dimensional grating. When X-rays are irradiated to the body, each atom scatters X-rays, and the scattered X-rays of each atom interfere with each other. When certain conditions are met, diffraction occurs. Figure: The condition for diffraction is that the optical path difference between the two layers is an integer multiple of the wavelength.
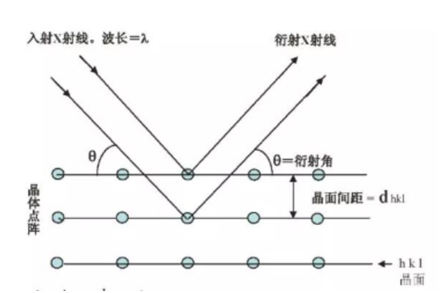
The crystal has different crystal faces, and different product faces have different product face spacing, as shown in the figure d1 and d2d3, and their respective shooting angles are different. The intensity of the fire is different. Different crystals, the atoms are arranged differently, the composition is different, and the diffraction is different. The actual crystal is a three-dimensional array of points, and diffraction is also generated in three-dimensional space.
![]()
2. Polycrystal diffraction, diffraction pile
The position of a (k) plane of a grain exactly conforms to Bragg's formula, resulting in diffraction. Figure 1
Polycrystals are aggregates of very many small grains. If the orientation of each grain is randomly distributed, it is equivalent to any rotation of the crystal surface around the incident X-ray beam in the above figure. Then, when the X-ray is irradiated on the polycrystal, diffraction lines are generated on a conical surface in the figure. Figure 2
If a detector is rotated along the equator, this diffraction line can be detected when it is turned to the 20 Angle. Figure 3
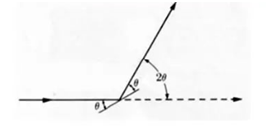
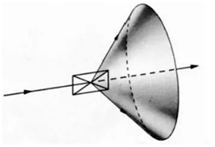
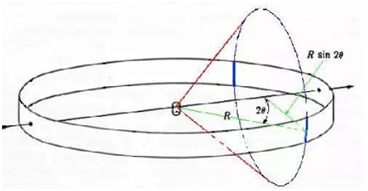
Figure 1 Figure 2 Figure3


X-ray Single Crystal Diffractometer X-ray Crystal Analyzer

