- Home
- >
News
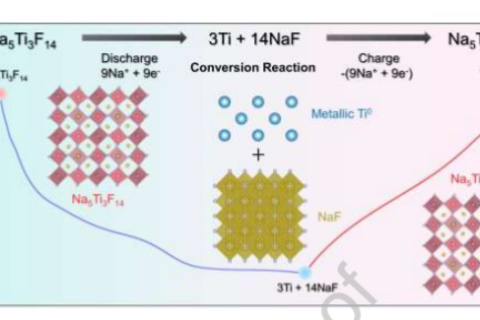
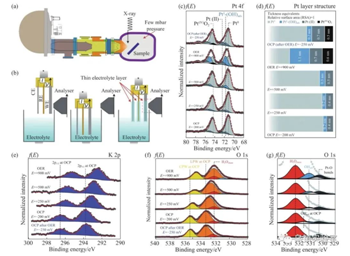
Sungkyunkwan University in South Korea has demonstrated that nano-Na5Ti3F14 / carbon nanocomposites have excellent electrochemical properties as the negative electrode of sodium-ion batteries.
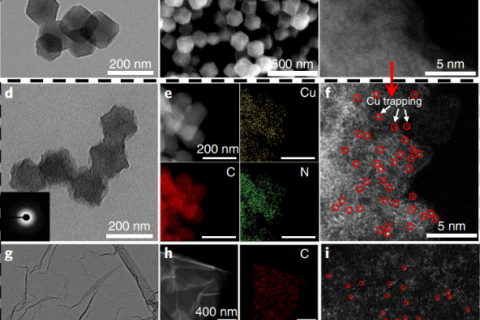
Characterization methods of copper monatomic catalysts are often used to determine their structure and properties, and the following are several common characterization methods.
Cement is a common building supplies, generally divided into ordinary Portland cement, Portland cement mixed materials and special cement, the use of Portland cement is more.
Recently, Applied Clay Science reported "High-pressure Raman scattering and X-ray diffraction study of kaolinite, Al2Si2O5(OH)4."
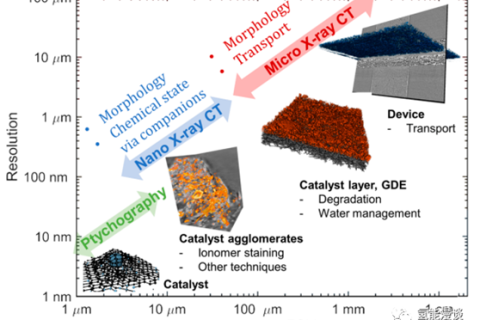
In recent years, with the demand for clean energy and the development of a net zero greenhouse gas emission economy, the field of electrocatalysis has attracted great interest.
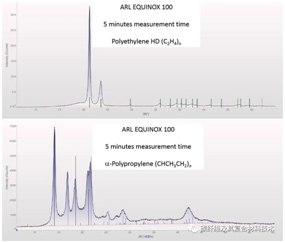
The main indicators of polymer materials include the type of polymer or its crystallinity. Polymers also exhibit different microstructure, which can also affect the mechanical .properties of polymer materials.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is a means of research to obtain information such as the composition of a material, the structure or form of an internal atom or molecule by analyzing its diffraction pattern through X-ray diffraction.
Crystals, although long admired for their regularity and symmetry, were not studied scientifically until the 17th century. Let's take a look at the early history of crystallography.
Using the principle of X-ray diffraction, the cutting Angle of natural and artificial single crystals is accurately and quickly determined, and the cutting machine is equipped for directional cutting of the said crystals.
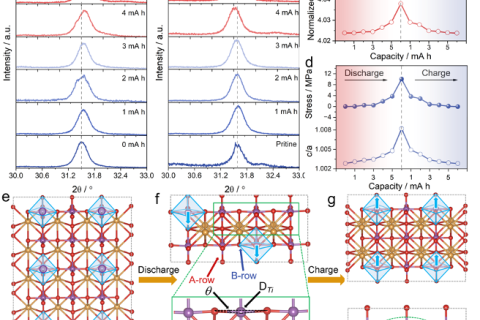
The method of assisting internal stress without additional energy proposed in this paper provides an economical and convenient new strategy for improving battery reaction dynamics.
XRD can measure bulk and powder samples, and has different requirements for different sample sizes and properties.
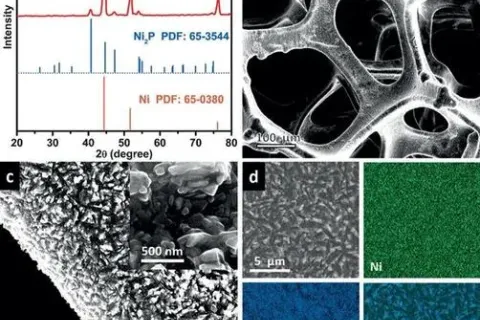
Taking deposition scaling as an example, this paper introduces how to use X-ray diffractometer for qualitative phase and quantitative analysis.