- Home
- >
News
Powder X-ray diffraction, as one of the methods for the study of drug polymorphism, has the advantages of no sample destruction and simple operation.
In the past 10 years, the Institute of Physics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has used powder diffraction method to determine the crystal structure of many inorganic and organic compounds.
As one of the important means of material structure characterization, XRD is widely used in materials, physics, chemistry, medicine and other fields.
X-ray diffractometer is a device that uses the principle of interaction between X-rays and substances to obtain information such as crystal structure and lattice constant of substances by measuring the diffraction Angle and intensity of X-rays in substances.
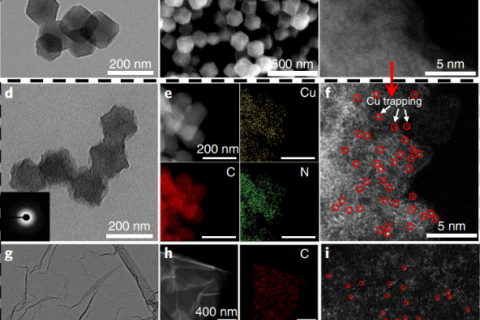
Characterization methods of copper monatomic catalysts are often used to determine their structure and properties, and the following are several common characterization methods.
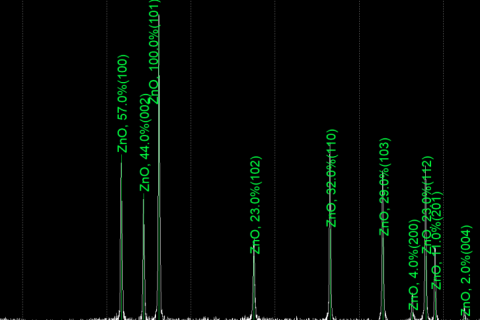
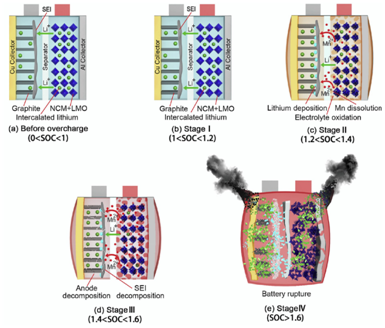
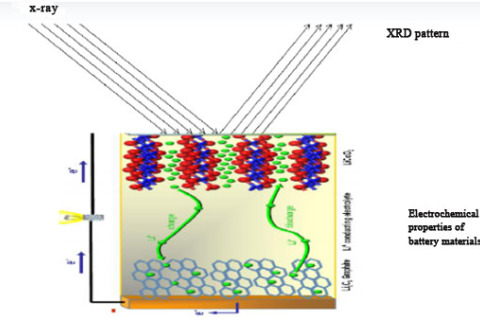
X-ray diffraction technology is widely used in the research of lithium-ion batteries. XRD is a conventional method for qualitative and quantitative analysis of phases in materials.
The application of new technologies and new products such as 5G, big data, and artificial intelligence will bring a huge semiconductor market demand, and global semiconductor equipment spending has entered an upward cycle.
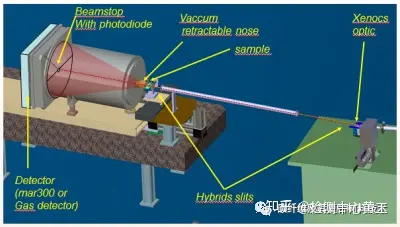
X-ray diffractometer (XRD) can be divided into X-ray powder diffractometer and X-ray single crystal diffractometer, the basic physical principle of the two is the same.
XRD is a means of research which is Diffraction by X-Ray diffraction of a material to analyze its diffraction pattern to obtain information such as the composition of the material, the structure or shape of atoms or molecules inside the material.
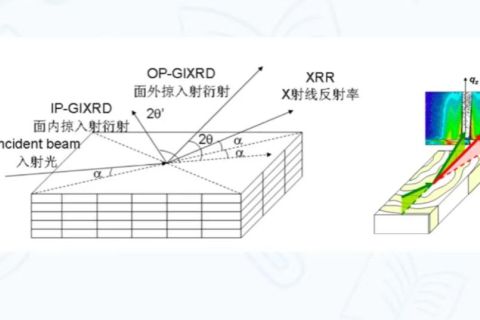
Grazing-incidence X-ray diffraction (GI-XRD) is a kind of X-ray diffraction technique, which is different from the traditional XRD experiment, mainly by changing the Angle of X-ray incidence and the orientation of the sample.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) is currently a powerful method for studying crystal structure (such as the type and location distribution of atoms or ions and their groups, cell shape and size, etc.).