- Home
- >
News
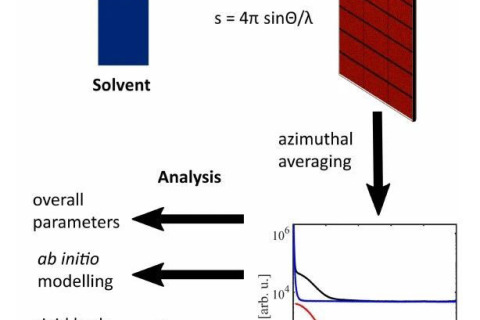
In recent years, X-ray small Angle scattering technique of biological macromolecules has been widely paid attention to. This article will mainly introduce the relevant progress of the combination of biological small Angle and other techniques in recent years.
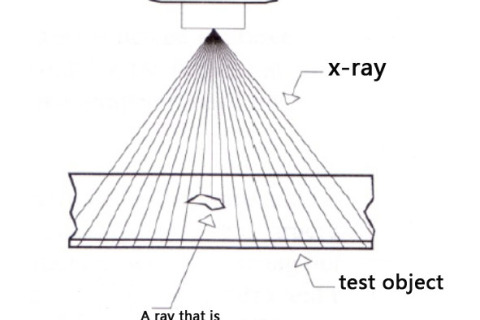
Nondestructive testing is based on the development of modern science and technology. With the development of modern industry, the application of non-destructive testing is more and more popular.
X-rays are a type of electromagnetic radiation widely used in medical and industrial fields. Although most X-rays are produced artificially, there are also some phenomena in nature that produce X-rays.
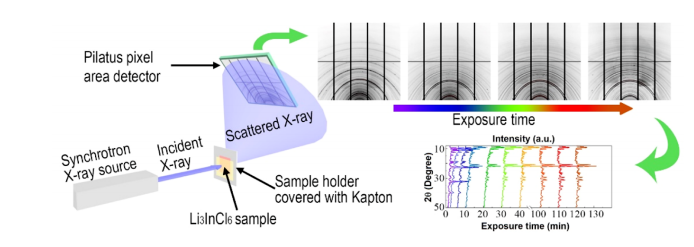
Based on Bragg's Law, in-situ X-ray diffraction (XRD) can be used to monitor the change of phase and its lattice parameters in the electrode or electrode-electrolyte interface in real time during the charge-discharge cycle of a battery.
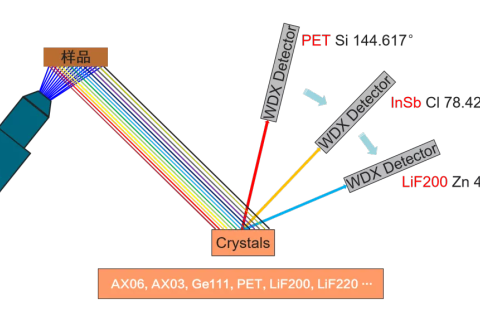
XRF instruments use X-rays to "excite" a material in order to characterize its composition by identifying elements in the sample (qualitative analysis) or by determining the strength of an element in the sample (quantitative analysis)
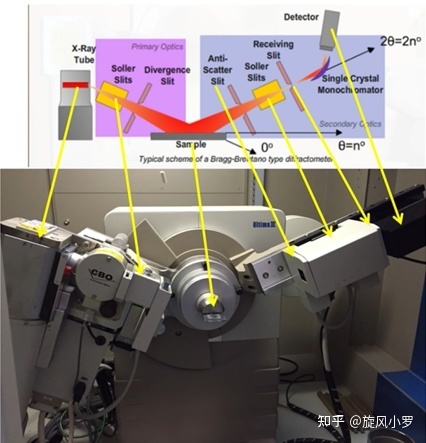
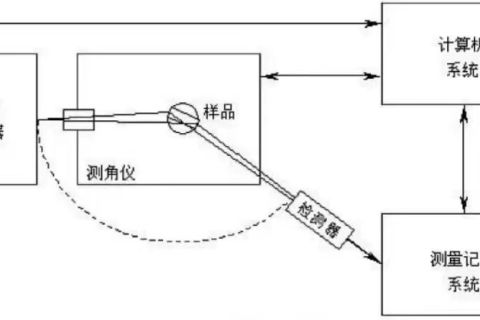
X-ray diffraction is the most effective and most widely used means, and X-ray diffraction is the first method used by humans to study the microstructure of matter.
X-rays are a type of short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation, between ultraviolet and gamma rays, that was developed by the German physicist W.K. It was discovered by Roentgen in 1895, so it is also called Roentgen rays.
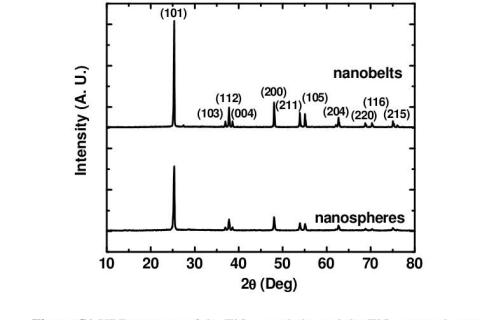
When X-ray diffraction is projected into a crystal as an electromagnetic wave, it is scattered by the atoms in the crystal, and the scattered waves appear to emanate from the center of the atoms, and the scattered waves emitted from the center of each atom are similar to the source spherical waves.