
About X-ray nondestructive testing
2023-09-08 10:00Nondestructive testing is based on the development of modern science and technology. With the development of modern industry, the application of non-destructive testing is more and more popular.Modern non-destructive testing is defined as: under the premise of not damaging the specimen, the use of physical or chemical methods as a means, with the help of cash technology and equipment, the internal and surface structure, properties of the inspection and testing, and the status of the specimen method.
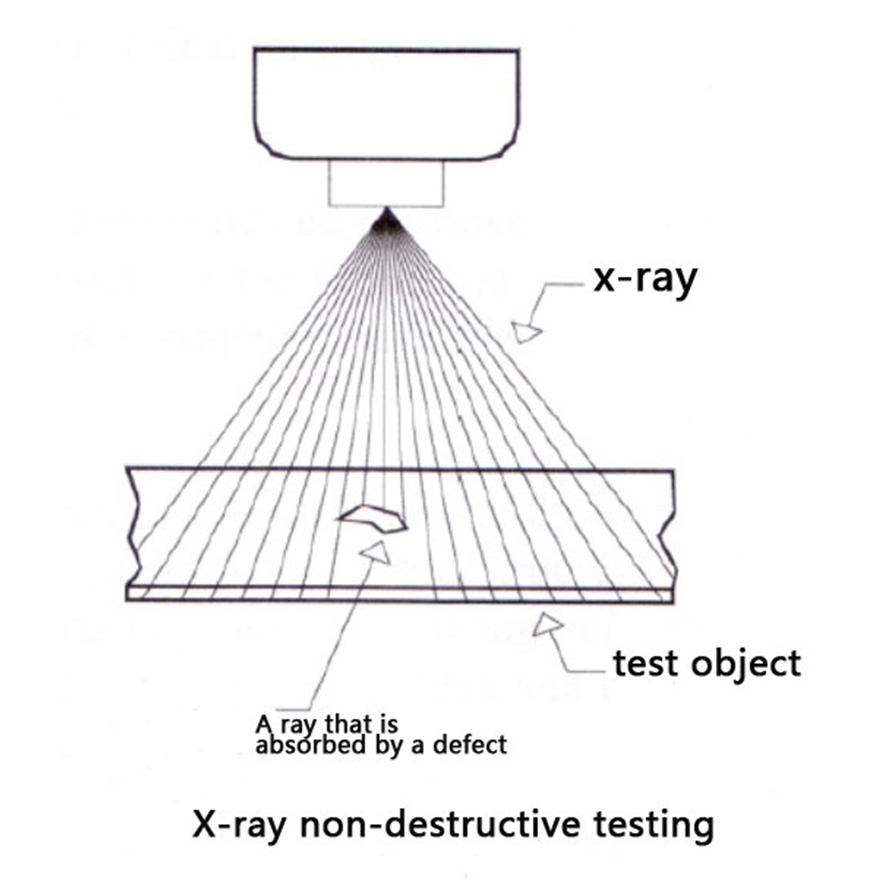
1.Radiographic examination. When penetrating each part of the object under test, defects in the object under test are detected using X-rays or gamma rays by exploiting differences in intensity attenuation. If the absorbed light is projected onto the X-ray film, after development, a photograph showing changes in the thickness of the object and internal defects can be obtained. If you use a fluorescent screen instead of film, you can directly observe the internal condition of the object being examined.
2.Ultrasonic test. The influence of the acoustic characteristics of the object itself or the defects on the ultrasonic propagation is used to detect the defects or some physical characteristics of the object. The ultrasound frequency commonly used in ultrasonic testing is 0.5 to 5 MHz. The most commonly used ultrasound test is the pulse test.
3.Acoustic emission detection. The performance or structural integrity of a material is evaluated by receiving and analyzing its acoustic emission signals. The phenomenon of rapid release of strain energy caused by stress waves caused by crack propagation, plastic deformation or phase transition in a material is called acoustic emission. The acoustic emission generated by the material under the action of external factors is received by the acoustic sensor and converted into an electrical signal, which is amplified and sent to the signal processor to measure various characteristic parameters of the acoustic emission signal.
4.Penetration testing. The permeability of certain liquids is used to narrow gaps to detect surface defects. Commonly used penetrants are liquids containing colored dyes or fluorescence.
5.Magnetic particle inspection. In order to detect defects on or near the surface of the target through the accumulation of magnetic particles in the leakage magnetic field near the target defect, the target to be detected must be ferromagnetic. In addition, new NDT technologies such as neutron radiography, laser holography, ultrasonic holography, infrared detection and microwave detection have also been developed and applied.

