- Home
- >
- News
- >
- Industry news
- >
News
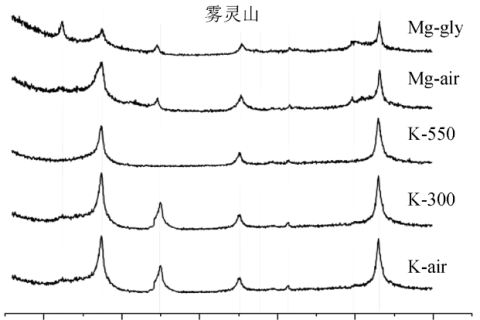
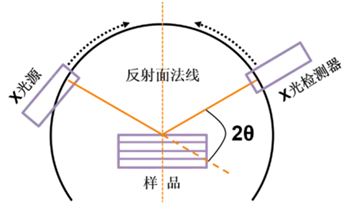
The X-ray diffraction pattern serves as the most reliable foundation for determining polycrystalline patterns, and the X-ray diffraction pattern is frequently regarded as the "fingerprint" of crystalline patterns.
The crystal structure of the perovskite films modified by ionic liquid (ILs) BMIMAc under various annealing durations was characterized by X-ray diffraction.
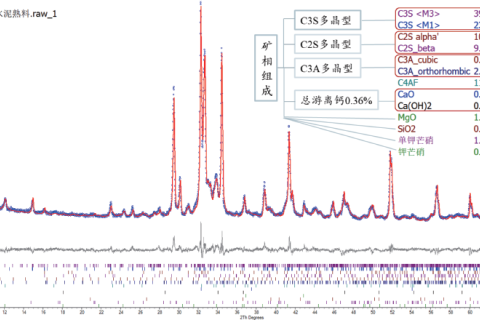
As an indispensable raw material in the realm of construction, cement assumes a vital role throughout the construction process. There exist numerous types of Portland cement. Owing to its superb performance, Portland cement is extensively utilized.
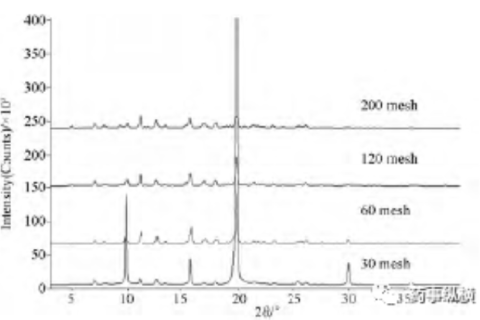
X-ray diffraction is a fast, accurate and efficient non-destructive testing technique for materials. As a means of characterizing the crystal structure and its change rule, it is widely used in many fields such as biology, medicine, ceramics and so on.
X-ray diffractometer is a kind of instrument to analyze the crystal structure, phase composition and crystal orientation of a substance by the interaction of X-ray with matter.
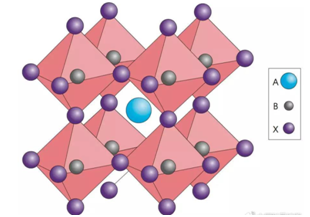
The properties of materials are often determined by their phase composition, and XRD is widely used as one of the main means of phase analysis.
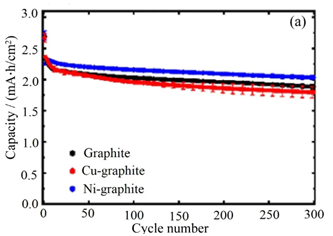
The degree of graphitization refers to how closely the crystal structure of the graphite material resembles perfect graphite after rearranging the amorphous carbon structure.
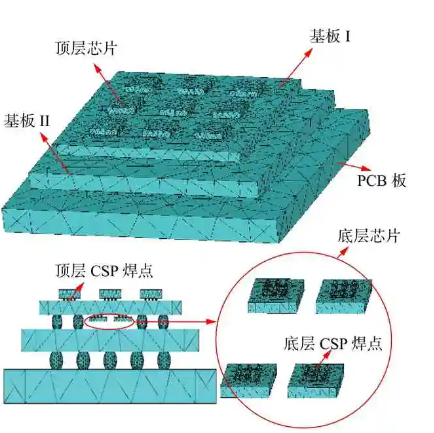
An X-ray stress diffractometer is a widely utilized instrument in the field of materials science and engineering for measuring the internal stress distribution of materials.
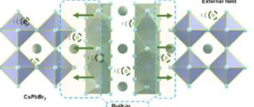
A research team from the Hefei Institute of Physical Sciences at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has recently conducted a study proposing a novel method to improve X-ray detection by incorporating out-of-phase CsPb2Br5 peritectic crystals into CsPbBr3 block materials.