- Home
- >
- News
- >
- Industry news
- >
News
This article mainly shares some relevant issues about "JADE software analysis and processing XRD data".
X-ray diffraction is the most effective and most widely used means, and X-ray diffraction is the first method used by humans to study the microstructure of matter.
X-rays are a type of short-wavelength electromagnetic radiation, between ultraviolet and gamma rays, that was developed by the German physicist W.K. It was discovered by Roentgen in 1895, so it is also called Roentgen rays.
X-ray diffraction technology is widely used in chemical industry, scientific research, material production and other fields because of its nondestructive, pollution-free, fast, high measurement accuracy and large amount of information about crystal integrity.
When X-ray diffraction is projected into a crystal as an electromagnetic wave, it is scattered by the atoms in the crystal, and the scattered waves appear to emanate from the center of the atoms, and the scattered waves emitted from the center of each atom are similar to the source spherical waves.
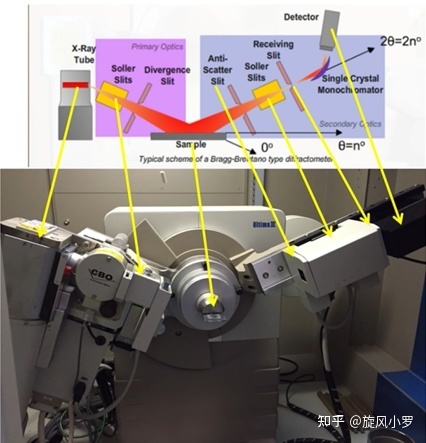
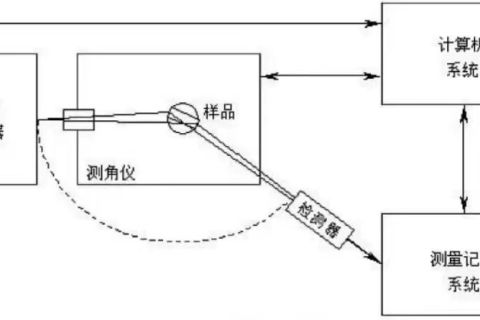
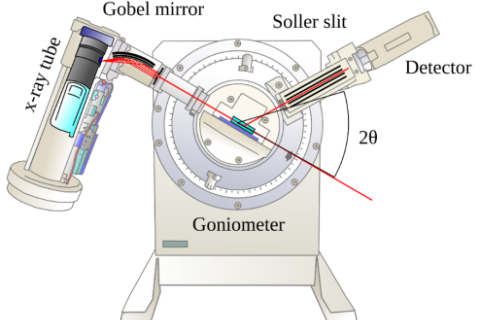
X-ray diffractometer , also known as X-ray crystal diffractometer, abbreviated XPD or XRD, is an instrument to study the internal microstructure of matter. X-ray diffractometer has the advantages of high precision, high stability and convenient operation.
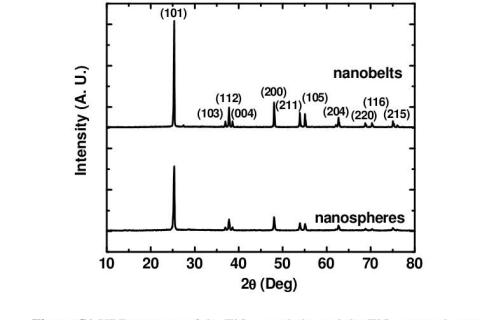
X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) is a major method for studying the phase and crystal structure of a substance. When a substance (crystal or non-crystal) is diffraction analysis, the substance is irradiated by X-rays to produce different degrees of diffraction phenomenon, material composition, crystal type, intramolecular bonding mode, molecular configuration, conformation and other material characteristics determine the specific diffraction pattern of the substance.