- Home
- >
News
As an indispensable raw material in the realm of construction, cement assumes a vital role throughout the construction process. There exist numerous types of Portland cement. Owing to its superb performance, Portland cement is extensively utilized.
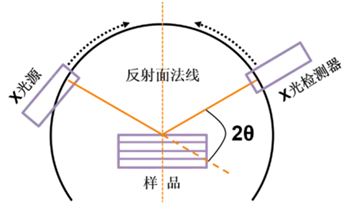
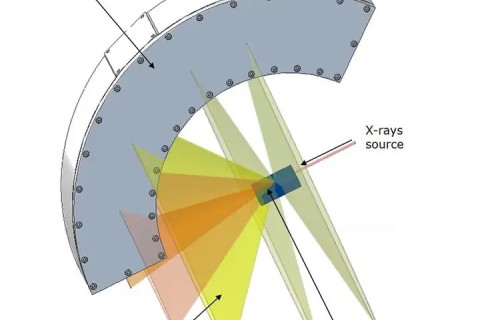
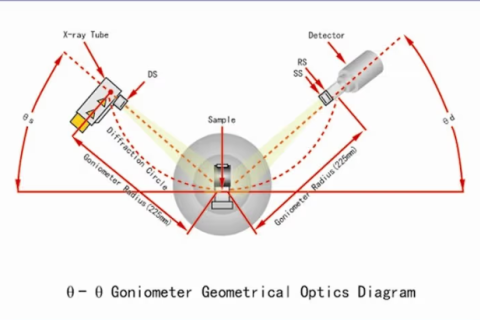
X-ray diffractometer is a kind of instrument to analyze the crystal structure, phase composition and crystal orientation of a substance by the interaction of X-ray with matter.
XRD is the most advanced X-ray diffractometer system in the world today, with precise design and complete functions, and can flexibly adapt to various microstructure determination such as powder.
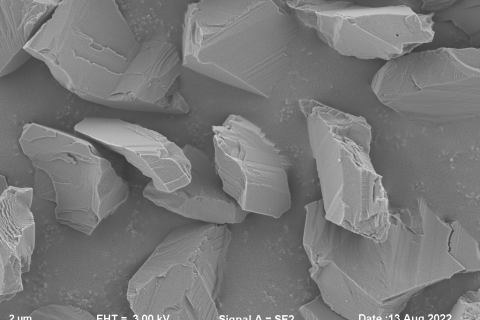
Different crystal forms of the same drug may differ significantly in appearance, solubility, melting point, etc., affecting the stability, production, bioavailability, and safety of the drug.
X-ray diffraction is a method to study the phase and crystal structure of a substance by using the diffraction phenomenon of X-rays in a crystal.
X-ray diffraction is a method of analyzing the structure or composition of a sample by shining a monochromatic X-ray beam on it.
In-situ XRD, also known as In situ X-ray Diffraction, is a technique for making X-ray diffraction measurements during a structure or phase transition. This technology can monitor the dynamic change of the structure of the material under external force in real time.
Powder X-ray diffraction, as one of the methods for the study of drug polymorphism, has the advantages of not destroying samples and simple operation, and is the main method for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of drug polymorphism at present.
This paper introduces the related knowledge of crystal pattern and crystal fetish
Powder X-ray diffraction, as one of the methods for the study of drug polymorphism, has the advantages of no sample destruction and simple operation.