- Home
- >
News
New-generation HR-XRD cuts energy use via hardware upgrades, smart controls, and full lifecycle management, maintaining precision while slashing costs and emissions for green labs.
This guide details essential maintenance for benchtop XRD systems, covering X-ray generation, optics, detectors, and safety. Regular upkeep ensures accuracy, prevents failures, and extends equipment life. The TDM-20 Benchtop XRD from Dandong Tongda Technology meets all your analytical needs.
XRD maintenance follows "Prevention First, Regular Inspection." Safety protocols require "Protection Priority, Standardized Procedures." Key practices include environment control, component care, strict safety checks, and proper shutdown. Adherence ensures instrument longevity, operator safety, and data reliability.
Benchtop diffractometers enable rapid, on-site phase identification. Their compact size and simple operation overcome traditional XRD limitations, boosting efficiency in QC, R&D, and field applications like material screening and analysis.
A premier X-ray crystal analyzer enabling precise exploration of material microstructures. Its advanced PLC control, modular design, and robust 5KW output ensure high reliability for global R&D and industrial quality control applications.
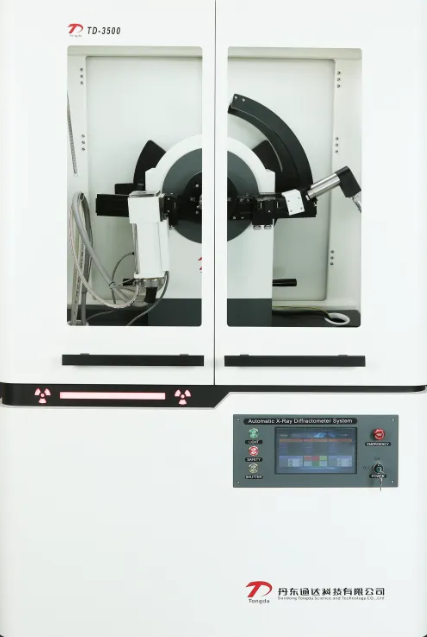
The TD-3500 X-ray Diffractometer ensures stable operation through full-chain PLC automation and a high-precision goniometer with real-time error correction, achieving exceptional angular reproducibility. It offers flexible configurations for diverse applications and performs comprehensive analyses across various critical fields.
The TD-3700 is a next-gen X-ray diffractometer featuring a high-speed array detector for intensity scores of times higher and rapid, noise-free analysis. Its transmission mode excels with trace samples. Modular and one-touch, it ensures easy operation and global compliance for diverse lab applications worldwide.
The TDM-20 benchtop XRD redefines performance standards with a groundbreaking 1200W power core—double the mainstream level. This enables faster, more precise analysis from R&D to QC in pharmaceuticals, materials science, mining, and food safety.
Dandong Tongda Science & Technology Co., Ltd., achieved a breakthrough by independently developing the TD-5000 X-ray single crystal diffractometer through collaboration with Academician Chen Xiaoming. This success, stemming from a national R&D project, signifies China's leap in high-end scientific instruments, gaining both domestic and international market recognition.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) uses Bragg's Law to analyze material structures by measuring diffraction angles. Dandong Tongda's product line, from the versatile TD-3500 and advanced TD-3700 to the compact TDM-20, provides complete solutions for education, industry, and cutting-edge research.
Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. is a high-tech enterprise from China specializing in X-ray analysis and NDT equipment. With core competitiveness in XRD, we provide precise tools for global research and industry.
Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd., a leading Chinese manufacturer of analytical instruments, is proud to present its flagship product to the global market: the TD-3500 X-ray Diffractometer (XRD). Meticulously engineered with cutting-edge technology and precision craftsmanship, the TD-3500 is designed to deliver an exceptional analytical experience for global research institutions, university laboratories, and industrial quality control departments. The TD-3500 is far from an ordinary X-ray diffractometer. It embodies Tongda Technology's profound technical expertise and deep understanding of user needs. Designed around the core principles of "Precise, Efficient, Stable, and User-friendly," it is committed to becoming your most reliable laboratory partner. This high-precision instrument is widely used in material analysis and excels at in-depth microstructural analysis of powders, bulk solids, and thin films. Core Technical Specifications & Features High-Stability X-Ray Generator: Utilizes an imported PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) for precise control. With a rated power of up to 5kW, wide tube voltage and current ranges (10-60kV, 2-80mA), and an output stability better than 0.01%, it guarantees exceptionally stable and reliable data acquisition. High-Precision Goniometer: The heart of the diffractometer features imported high-precision bearings and a fully closed-loop vector drive servo system. It offers extremely high angular reproducibility (minimum step size of 0.0001 degrees), ensuring unparalleled measurement accuracy. Its vertical (θ-θ) design keeps the sample stationary and horizontal during testing, making it suitable not only for solids but also for challenging states like liquids, gels, and viscous samples. Low-Noise Detection & Counting System: Equipped with high-performance proportional or scintillation counters, the system boasts a wide counting linear range (≥700,000 cps) with very low background noise (≤1 cps), effectively capturing weak diffraction signals for enhanced data accuracy. Comprehensive Safety Protection: Safety is paramount. The TD-3500 is equipped with a dual protection system: the shutter interlock is linked to the lead door. If the door is accidentally opened, the shutter closes automatically, high voltage drops to a safe level, and data acquisition halts immediately, maximizing operator safety. Radiation leakage is significantly below national standards. Powerful Analysis Software & Database: The system includes robust software for data collection and processing, integrated with professional analysis tools like Jade and the PDF database. Notably, it features a dedicated measurement program for the titanium dioxide industry, enabling rapid and accurate analysis of Rutile and Anatase content with errors controlled within 0.2%. Key Competitive Advantages of the TD-3500 1. Exceptional Performance & Precision High Resolution & Intensity: An optimized optical path and highly stable X-ray generator ensure high-resolution, high signal-to-noise ratio diffraction patterns. It delivers impeccable data quality for both qualitative/quantitative phase analysis and precise lattice parameter calculations. Robust Stability: Core components feature a fully enclosed protective design, coupled with a precise temperature control system. This ensures ultra-high stability and data reproducibility during long-term continuous operation, meeting the most stringent demands of industrial online detection. 2. Intelligent & User-Friendly Operation One-Click Smart Operation: The new-generation intelligent control software features an intuitive interface and smooth operation. Even novice users can easily complete complex testing tasks using pre-set programs, significantly reducing the learning curve and operational barriers. Powerful Data Analysis Capabilities: The software incorporates a powerful database and advanced analysis algorithms, enabling rapid phase identification, crystallite size and microstrain calculation, residual stress analysis, and more, helping you extract key insights from vast amounts of data quickly. 3. Wide Applicability & Flexibility The TD-3500 effortlessly handles samples of various forms—powder, bulk, thin film—finding applications across diverse fields such as new material R&D, metallurgy, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, cement, ceramics, geological exploration, and cultural heritage authentication. Its modular design also allows for future functional expansions, protecting your investment. 4. Rugged Construction & Global Support Built with meticulous attention to detail and superior materials, the TD-3500 ensures stable operation in various complex environments worldwide. Furthermore, Dandong Tongda Technology Co., Ltd. has established a comprehensive global sales and service network, providing professional pre-sales consultation, technical training, and timely after-sales support to ensure peace of mind for customers anywhere in the world. Our Commitment With years of deep expertise in the X-ray analysis instrument field, we understand the unique challenges each customer faces. The launch of the TD-3500 X-ray Diffractometer represents not only the pinnacle of our technology but also our commitment to empowering global customer success. "We are dedicated to bringing the world's scientists and engineers the most reliable technological tools through continuous innovation," said the General Manager of Tongda Technology. "The TD-3500 X-ray Diffractometer is our sincere offering to the market. We believe it will become a powerful engine for our customers to explore material mysteries, enhance product quality, and drive technological revolution."