- Home
- >
- News
- >
- Leading the New Era
- >
Leading the New Era
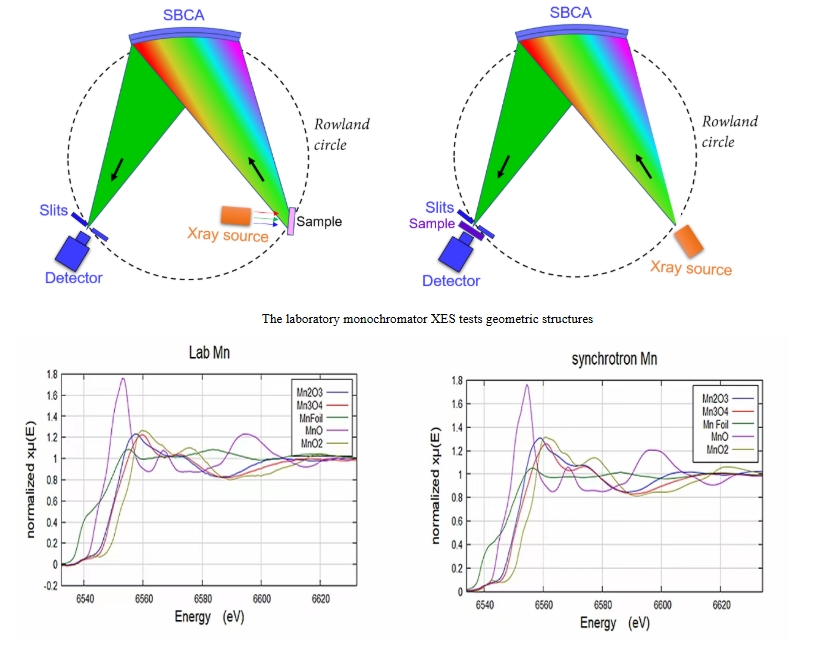
2025-04-17 10:39X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer (XAFS) is a powerful tool for studying the local atomic or electronic structure of materials, widely used in popular fields such as catalysis, energy, and nanotechnology.
The basic principle of X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer (XAFS) is that when the energy of X-rays resonates with the energy of an inner electron shell of an element in the sample, a sudden increase in electrons is excited to form a continuous spectrum, which is called the absorption edge. Near the absorption edge, as the X-ray energy increases, the absorption rate monotonically decreases as the penetration depth of the X-ray increases. When the spectrum is extended beyond a specific edge, fine structures can be observed, where X-ray absorption near edge structures (XANES) regions appear as soon as peaks and shoulders with a width exceeding 20 to 30 electron volts pass through the starting point of the edge. The fine structure located on the high-energy side of the edge where energy decays to several hundred electron volts is called X-ray Absorption Fine Structure (XAFS).
The main features of X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer (XAFS) are:
Sensitivity to short-range ordering: It depends on short-range ordering and does not rely on long-range ordering, making it possible to measure a wide range of samples. It can be used for amorphous, liquid, molten, catalyst active centers, metal proteins, etc., as well as for structural studies of impurity atoms in crystals.
Strong elemental characteristics: The X-ray absorption edge has elemental characteristics, and for atoms of different elements in the sample, the atomic neighbor structure of different elements in the same compound can be studied by adjusting the incident X-ray energy.
High sensitivity: Fluorescence method can be used to measure samples of elements with concentrations as low as one millionth.
Comprehensive acquisition of structural information: able to provide parameters that determine the local structure, such as the distance between absorbing atoms and neighboring atoms, the number and type of these atoms, and the oxidation state of absorbing elements.
Sample preparation is simple: no single crystal is required, and under the experimental conditions, the data collection time is relatively short. Using a synchrotron X-ray source usually only takes a few minutes to measure a spectral line.
The main advantages of X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer (XAFS) are:
Core advantage: highest luminous flux product
Photon flux exceeding 1000000 photons/second/eV, with spectral efficiency several times higher than other products; Obtain data quality equivalent to synchrotron radiation
Excellent stability:
The stability of monochromatic light intensity of the light source is better than 0.1%, and the energy drift during repeated collection is less than 50 meV
1% detection limit:
High luminous flux, excellent optical path optimization, and excellent light source stability ensure that high-quality EXAFS data can still be obtained when the measured element content is>1%.
4. Application areas of X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer (XAFS) :
Energy field: such as research on lithium batteries and other secondary battery materials, fuel cell research, hydrogen storage material research, etc. XAFS can be used to obtain the concentration, valence state, coordination environment, and dynamic changes of core atoms during charge discharge cycles and electrochemical reactions.
Catalysis field: used for research on nanoparticle catalysis, single atom catalysis, etc. Obtain the morphology of the catalyst on the support, the interaction form with the support, and its changes during the catalytic process through XAFS, as well as the neighboring structures of metal ions with extremely low content.
In the field of materials science, X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer (XAFS) is used for the characterization of various materials, the study of complex systems and disordered structural materials, the research of radioactive isotopes, the study of related properties of surface and interface materials, and the study of dynamic changes in materials.
In the field of geology, X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer (XAFS) can be used for element valence state analysis of ore materials in geological research.
Environmental field: XES can be used for valence state analysis of Cr/As elements, etc.
In the field of radiochemistry, X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer (XAFS) can be used for valence state analysis of Ce, U elements, etc.
The X-ray absorption fine structure spectrometer (XAFS) plays an important role in modern scientific research due to its unique working principle, significant characteristics, and wide application fields. It provides a powerful means for people to gain a deeper understanding of the microstructure and chemical state of matter, promoting the development and progress of multiple disciplinary fields.