
X-ray diffraction analysis of graphite anode materials
2024-04-15 23:00When graphite materials are used in the negative electrode materials of lithium batteries, in addition to the analysis and detection of its element content, particle size and particle size distribution, there is a very important indicator that it is necessary to measure its graphitization degree.
The most common anode material in lithium-ion batteries is a crystalline graphite-like carbon material with a layered structure.
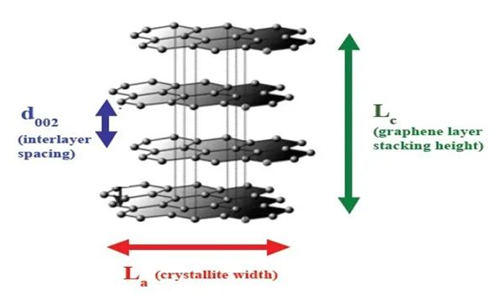
X-ray diffraction is a standard method for crystal structure determination, so it can also be used to measure the degree of graphitization of graphite anode materials.
After graphite electrode sheet is made, the orientation (orientation) of graphite layer structure also has a great influence on lithium ion migration.
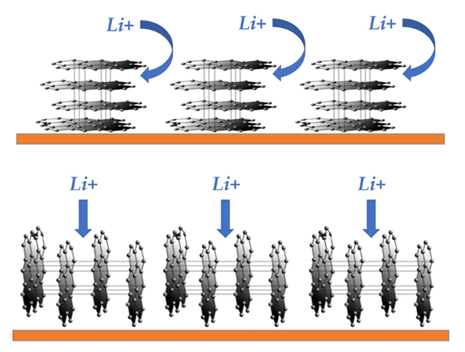
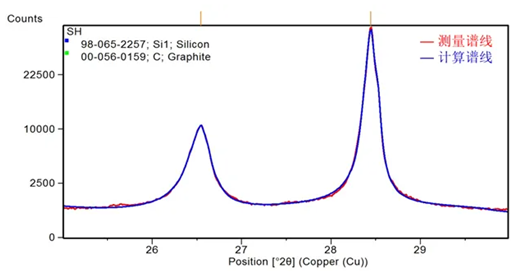
The X-ray diffraction method is also used to test the orientation of graphite electrodes. When conducting the diffraction pattern test on the electrode plate sample placed horizontally, the diffraction signal of the (110) crystal plane can be collected from the graphite whose layer structure is perpendicular to the electrode plate, and the diffraction signal of the (002) and (004) crystal plane is from the graphite whose layer structure is parallel to the electrode plate. The orientation of the graphite electrode can be described as the ratio of (002) or (004) diffraction peak intensity (or integral area) to (110) diffraction peak intensity.
