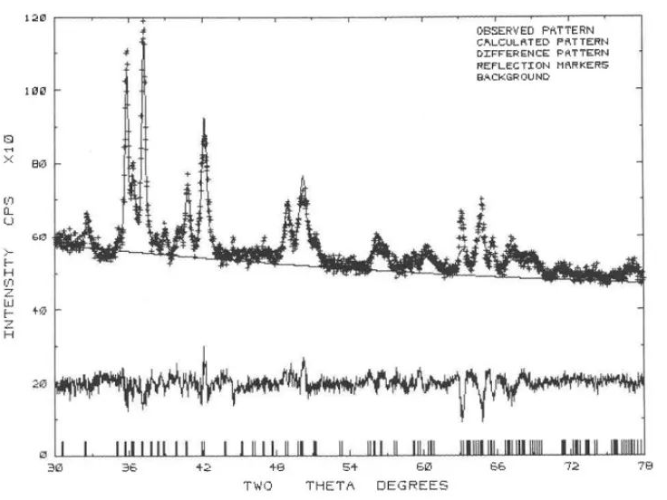
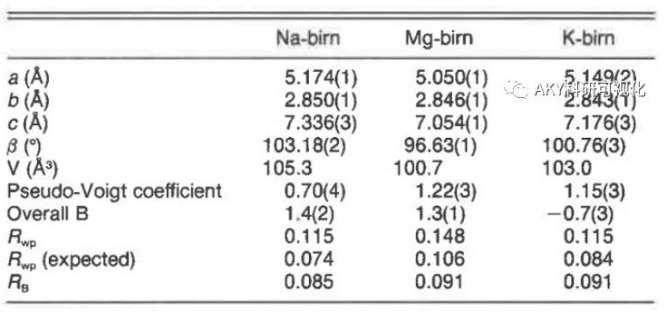
The crystal structure of Birnessite was determined
2024-01-29 10:00Manganite is a kind of manganese oxide with layered structure. It can exchange with a variety of cations (such as K*, Mg2+, Li*) to form a series of similar compounds. However, no matter it is naturally occurring or synthesized, the grain size of the material is very small or the crystallinity is very poor, so it is difficult to analyze its structure by single crystal diffraction method. To this end, David R. Verblen used X-ray powder line imaging technology combined with Rietveld refinement to determine the structures of several hydrosodium-manganese ores [1]. In view of the complex composition and poor crystallinity of natural minerals, the author adopted three kinds of synthetic hydromanganite (Na-,Mg-,and K-rich Birnessite) as the research object. Considering the layered structure of Chalcophanite, the Mn-0 layer in Chalcophanite is used as part of the initial crystal structure model of Chalcophanite. Fig1 shows the finishing map of Na-rich Birnessite. The final finishing results of the three hydrosodium-manganese ores are shown in Fig2: they are monoclinic C2/m structures, but have different cell parameters.