
Application of XRD in drug research
2024-03-20 23:00Sample mixing uniformity problem (for quantitative samples)
1. Grinding mixing (rotation/crystallinity change problem)
2. Dilution from high concentration to low concentration (uniformity of dilution concentration cannot be determined)
3. In the same sample, the particle size of different components is different. (Can not mix the sample after screening, need to complete the same mesh sieve, and then to mix.)
Multiple mixing method (for low concentration samples, content ≤1%)
Take 0.2% as an example, 3mg(monohydrate)+88.5mg (anhydrous)+ 1408.5mg
Due to the special mixing of trace samples, direct mixing is difficult to mix evenly! Need to mix in batches one by one!
Mixed step
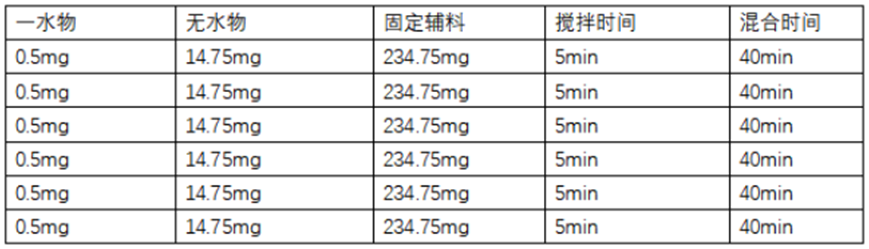
1. The total sample demand of this test can be weighed first, 3mg(water)+88.5mg (no water)+ 1408.5mg).
2. Then evenly divide the anhydrous API, one-water API and auxiliary materials into 6 parts
3. First, take one part, 0.5mg monoaqueous API, 14.75mg anhydrous and 234.75mg auxiliary materials, pour them into the centrifuge tube, gently stir them with a fine glass rod for about 5min to make them evenly mixed, and oscillate them in the whirlpool mixer for 40min.
4. Continue to take one part, 0.5mg monoaqueous API, 14.75mg anaqueous and 234.75mg auxiliary materials into the centrifugal tube, gently stir for about 5min to make it evenly mixed, and oscillate in the whirlpool mixer for 40min
5. And so on until the 6 portions are mixed

![]()

![]()




