
About the single point detector
2023-08-31 10:00一、Proportional Counter(PC)
PC generally uses a metal circle with an inner diameter of about 25mm as the cathode, and the center of the circle has a tungsten wire drawn into a straight line as the anode, and the cylinder is filled with 0.5~1atm of vapor or gas, and about 10% of the quenched gas (generally CH, ethanol or CI). The side wall or one end of the cylinder is provided with a window for incident X-rays. Because the X-rays used in diffraction experiments are mostly soft X-rays, the window wall is required to be extremely thin. The window material used is usually mica sheet or quilt.
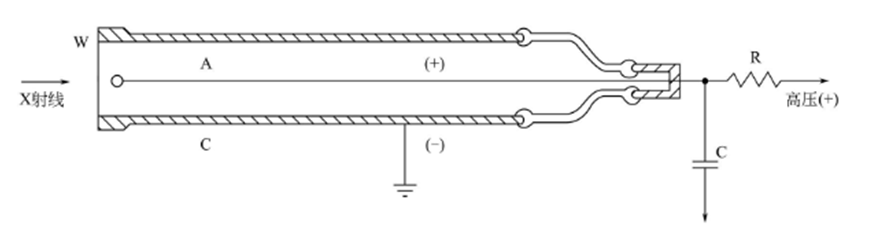
The PC works in the proportional region of the gas discharge in the tube. When using PC, a DC high voltage of 1000~2000V needs to be added between the two electrodes, depending on the discharge characteristics of the counter used. When a PC is irradiated by an X-ray, the gas in the tube is ionized, and the number of ion pairs initially produced is proportional to the quantum energy of the X-ray. Under the action of an appropriately high (proportional discharge region) electrode voltage, ions move in a directional manner and continuously collide with other neutral gas molecules in the process of movement, resulting in secondary or multiple ionization and accompanied by the photoelectric effect, at this time, the number of ionization is multiplied to form a limited discharge (an electron avalanche or gas discharge); When all the charges have accumulated on the corresponding electrode, the discharge stops. The time history of each discharge is very short, about 0.2~0.5ms. Therefore, every time an X-ray quantum enters the PC, a pulse current will pass between the poles. The average voltage drop (pulse voltage amplitude) generated by the pulse current on the load resistance is proportional to the quantum energy of the incident X-ray, so it is called proportional counter.When PC receives a single wavelength of radiation, the amplitude of the electrical pulse generated by each X-ray quantum is actually not strictly the same, but is distributed in a relatively narrow range centered on the average amplitude.
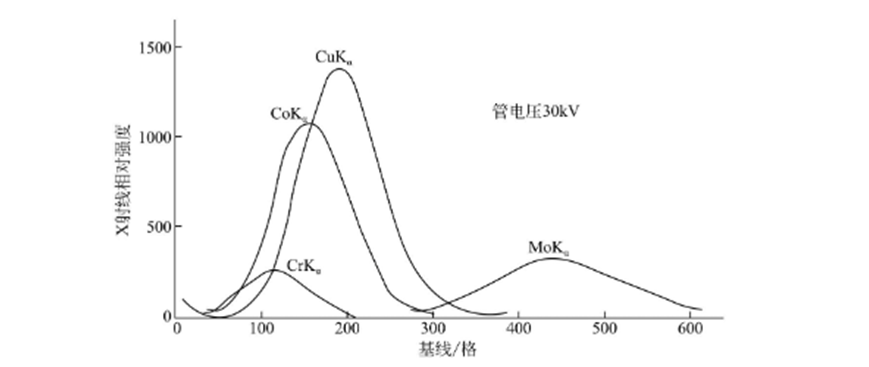
According to the discharge characteristics of PC, the average amplitude is determined by the quantum energy of the incident X-ray, and the narrower the width of the pulse amplitude distribution, the better the energy resolution.
二、Scintillation Counter(SC)
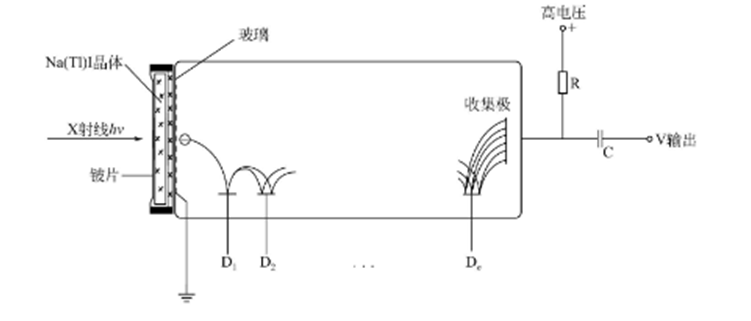
The scintillation counter (SC) used in X-ray diffraction analysis mostly uses Nal crystals doped with TI. The following diagram shows the basic structure of the scintillation counter, which consists of three parts: scintillation, photomultiplier and preamplifier.
Scintillator is a slice of Nal transparent single crystal doped with about 0.5% T as activator, about 1~2mm thick. The crystals are sealed in a special box to protect the Nal crystals from moisture damage. One side of the sealed box is a thin sheet (X-ray) that serves as a window for receiving X-rays; the other side is an optical glass sheet that is transparent to blue-violet light.
There is a multistage acceleration electrode inside, called the multiplier pole, the working time between the cathode and the collector (that is, the anode) to collect the photocurrent, the voltage through a voltage divider at the same time to each multiplier pole above, so that there is a voltage difference between each multiplier pole.
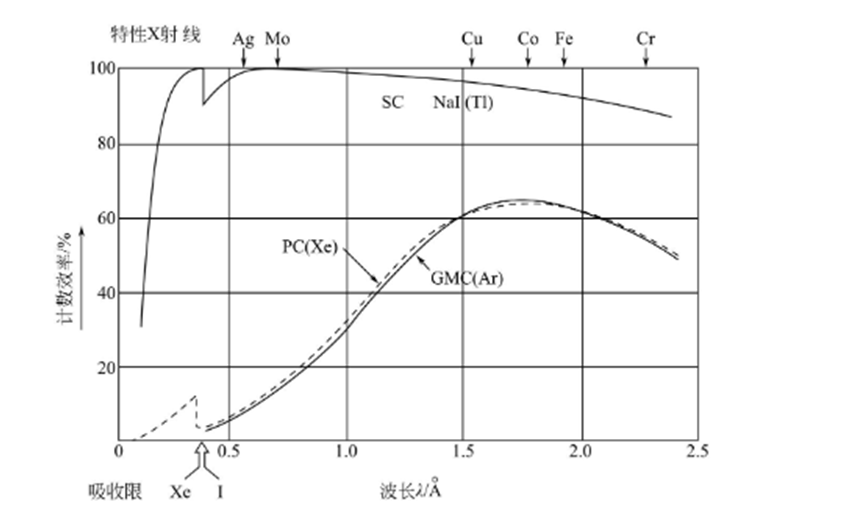
At present, SC is still the most versatile detector for various crystal X-ray diffraction work. Its main advantages are: for the various X-ray wavelengths used in crystal X-ray diffraction work, it has a high quantum efficiency of close to 100% good stability, long service life: in addition, it has a very short resolution time (on the order of 10-7s) like the proportional counter. Therefore, it is not necessary to consider the counting loss caused by the detector itself; It also has a certain energy resolution to the soft rays used for crystal diffraction. Therefore, most of today's X-ray radiographs are equipped with flash counters.
三、Semiconductor Detector(SDD)
1.Structure
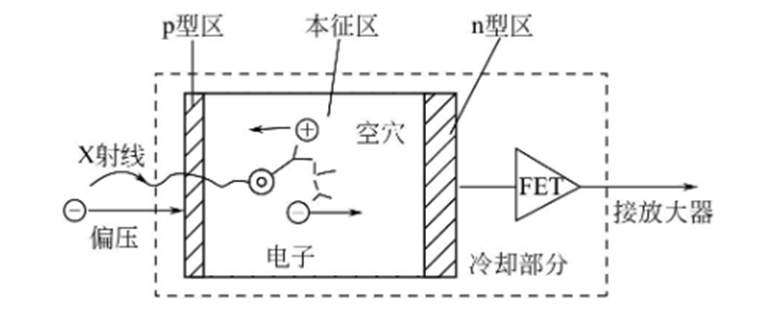
2. Working principle:When the X-ray irradiates the semiconductor, some electron-space six pairs can be produced due to the ionization of the ray quantum. Taking the structure of as an example, under the electric field between the electrodes, the electrons generated in the eigenregion of the electron-empty six pairs are concentrated in the n region, and the empty six is gathered in the p region. As a result, there will be a small pulse current flowing to the external circuit, and the eigenregion plays the role of [ionization box]. The energy required for SSD to be ionized to produce a pair of electron-empty six pairs is about 3.8eV, and the pulse resolution time of SSD is about 10-8s, so it is an extremely excellent detector.
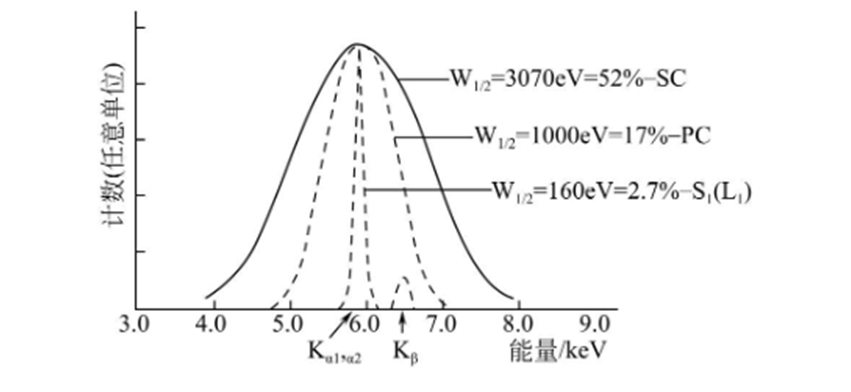
SSD can not only be used as a ray counter to measure the intensity of the ray, but also the energy of the ray. The high energy resolution SSD is used as an X-ray detector for a diffractometer and can also be used as an efficient (almost 100%)[monochromaticity] method. With the SSD's high energy resolution, only K is measured, avoiding the loss of strength and thereby increasing the intensity of X-ray reception several times. The use of SSD in X-ray radiometer can also achieve simultaneous X-ray radiographic and X-ray energy spectrum analysis, which is very valuable for phase analysis. These superior properties of SSDS have attracted attention in diffraction analysis, and high energy resolution SSDS are now listed as an option in the basic configuration of X-ray radiographs.
